Estimates the parameters of a given distribution and evaluates the probability density function with these parameters. This can be useful for comparing histograms or kernel density estimates against a theoretical distribution.
stat_theodensity(
mapping = NULL,
data = NULL,
geom = "line",
position = "identity",
...,
distri = "norm",
n = 512,
fix.arg = NULL,
start.arg = NULL,
na.rm = TRUE,
show.legend = NA,
inherit.aes = TRUE
)Arguments
- mapping
Set of aesthetic mappings created by
aes(). If specified andinherit.aes = TRUE(the default), it is combined with the default mapping at the top level of the plot. You must supplymappingif there is no plot mapping.- data
The data to be displayed in this layer. There are three options:
If
NULL, the default, the data is inherited from the plot data as specified in the call toggplot().A
data.frame, or other object, will override the plot data. All objects will be fortified to produce a data frame. Seefortify()for which variables will be created.A
functionwill be called with a single argument, the plot data. The return value must be adata.frame, and will be used as the layer data. Afunctioncan be created from aformula(e.g.~ head(.x, 10)).- geom
Use to override the default geom for
stat_theodensity.- position
A position adjustment to use on the data for this layer. This can be used in various ways, including to prevent overplotting and improving the display. The
positionargument accepts the following:The result of calling a position function, such as
position_jitter(). This method allows for passing extra arguments to the position.A string naming the position adjustment. To give the position as a string, strip the function name of the
position_prefix. For example, to useposition_jitter(), give the position as"jitter".For more information and other ways to specify the position, see the layer position documentation.
- ...
Other arguments passed on to
layer()'sparamsargument. These arguments broadly fall into one of 4 categories below. Notably, further arguments to thepositionargument, or aesthetics that are required can not be passed through.... Unknown arguments that are not part of the 4 categories below are ignored.Static aesthetics that are not mapped to a scale, but are at a fixed value and apply to the layer as a whole. For example,
colour = "red"orlinewidth = 3. The geom's documentation has an Aesthetics section that lists the available options. The 'required' aesthetics cannot be passed on to theparams. Please note that while passing unmapped aesthetics as vectors is technically possible, the order and required length is not guaranteed to be parallel to the input data.When constructing a layer using a
stat_*()function, the...argument can be used to pass on parameters to thegeompart of the layer. An example of this isstat_density(geom = "area", outline.type = "both"). The geom's documentation lists which parameters it can accept.Inversely, when constructing a layer using a
geom_*()function, the...argument can be used to pass on parameters to thestatpart of the layer. An example of this isgeom_area(stat = "density", adjust = 0.5). The stat's documentation lists which parameters it can accept.The
key_glyphargument oflayer()may also be passed on through.... This can be one of the functions described as key glyphs, to change the display of the layer in the legend.
- distri
A
characterof length 1 naming a distribution without prefix. See details.- n
An
integerof length 1 with the number of equally spaced points at which the density function is evaluated. Ignored if distribution is discrete.- fix.arg
An optional named list giving values of fixed parameters of the named distribution. Parameters with fixed value are not estimated by maximum likelihood procedures.
- start.arg
A named list giving initial values of parameters for the named distribution. This argument may be omitted (default) for some distributions for which reasonable starting values are computed.
- na.rm
If
FALSE, the default, missing values are removed with a warning. IfTRUE, missing values are silently removed.- show.legend
logical. Should this layer be included in the legends?
NA, the default, includes if any aesthetics are mapped.FALSEnever includes, andTRUEalways includes. It can also be a named logical vector to finely select the aesthetics to display.- inherit.aes
If
FALSE, overrides the default aesthetics, rather than combining with them. This is most useful for helper functions that define both data and aesthetics and shouldn't inherit behaviour from the default plot specification, e.g.borders().
Value
A Layer ggproto object.
Details
Valid distri arguments are the names of distributions for
which there exists a density function. The names should be given without a
prefix (typically 'd', 'r', 'q' and 'r'). For example: "norm" for
the normal distribution and "nbinom" for the negative binomial
distribution. Take a look at distributions() in the
stats package for an overview.
There are a couple of distribution for which there exist no reasonable
starting values, such as the Student t-distribution and the F-distribution.
In these cases, it would probably be wise to provide reasonable starting
values as a named list to the start.arg argument. When estimating a
binomial distribution, it would be best to supply the size to the
fix.arg argument.
By default, the y values are such that the integral of the distribution is
1, which scales well with the defaults of kernel density estimates. When
comparing distributions with absolute count histograms, a sensible choice
for aesthetic mapping would be aes(y = stat(count) * binwidth),
wherein binwidth is matched with the bin width of the histogram.
For discrete distributions, the input data are expected to be integers, or doubles that can be divided by 1 without remainders.
Parameters are estimated using the
fitdistrplus::fitdist() function in the
fitdistrplus package using maximum likelihood estimation.
Hypergeometric and multinomial distributions from the stats package
are not supported.
Computed variables
- density
probability density
- count
density * number of observations - useful for comparing to histograms
- scaled
density scaled to a maximum of 1
See also
Examples
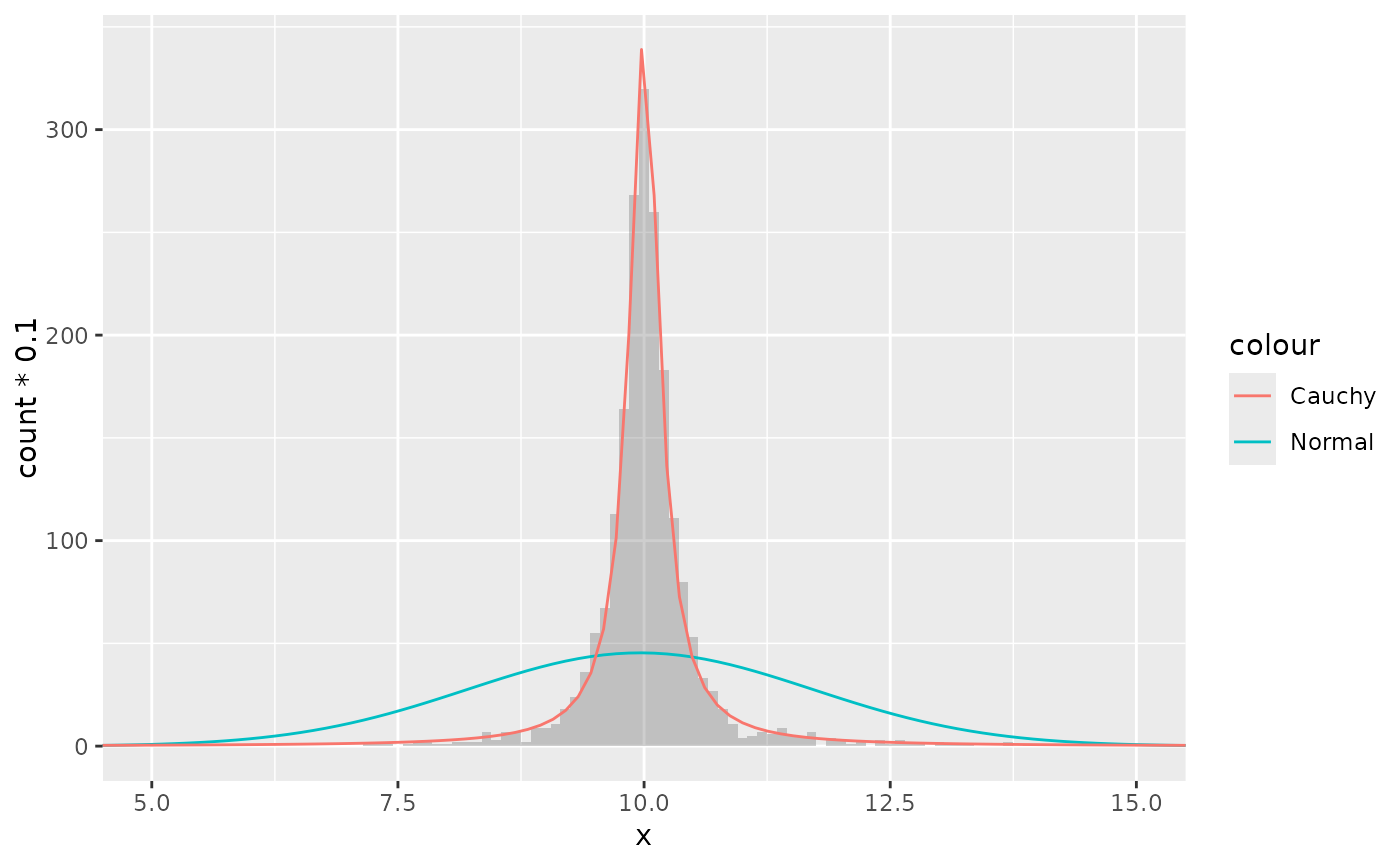
# A mixture of normal distributions where the standard deviation is
# inverse gamma distributed resembles a cauchy distribution.
x <- rnorm(2000, 10, 1/rgamma(2000, 2, 0.5))
df <- data.frame(x = x)
ggplot(df, aes(x)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 0.1,
alpha = 0.3, position = "identity") +
stat_theodensity(aes(y = stat(count) * 0.1, colour = "Normal"),
distri = "norm", geom = "line") +
stat_theodensity(aes(y = stat(count) * 0.1, colour = "Cauchy"),
distri = "cauchy", geom = "line") +
coord_cartesian(xlim = c(5, 15))
#> Warning: `stat(count)` was deprecated in ggplot2 3.4.0.
#> ℹ Please use `after_stat(count)` instead.
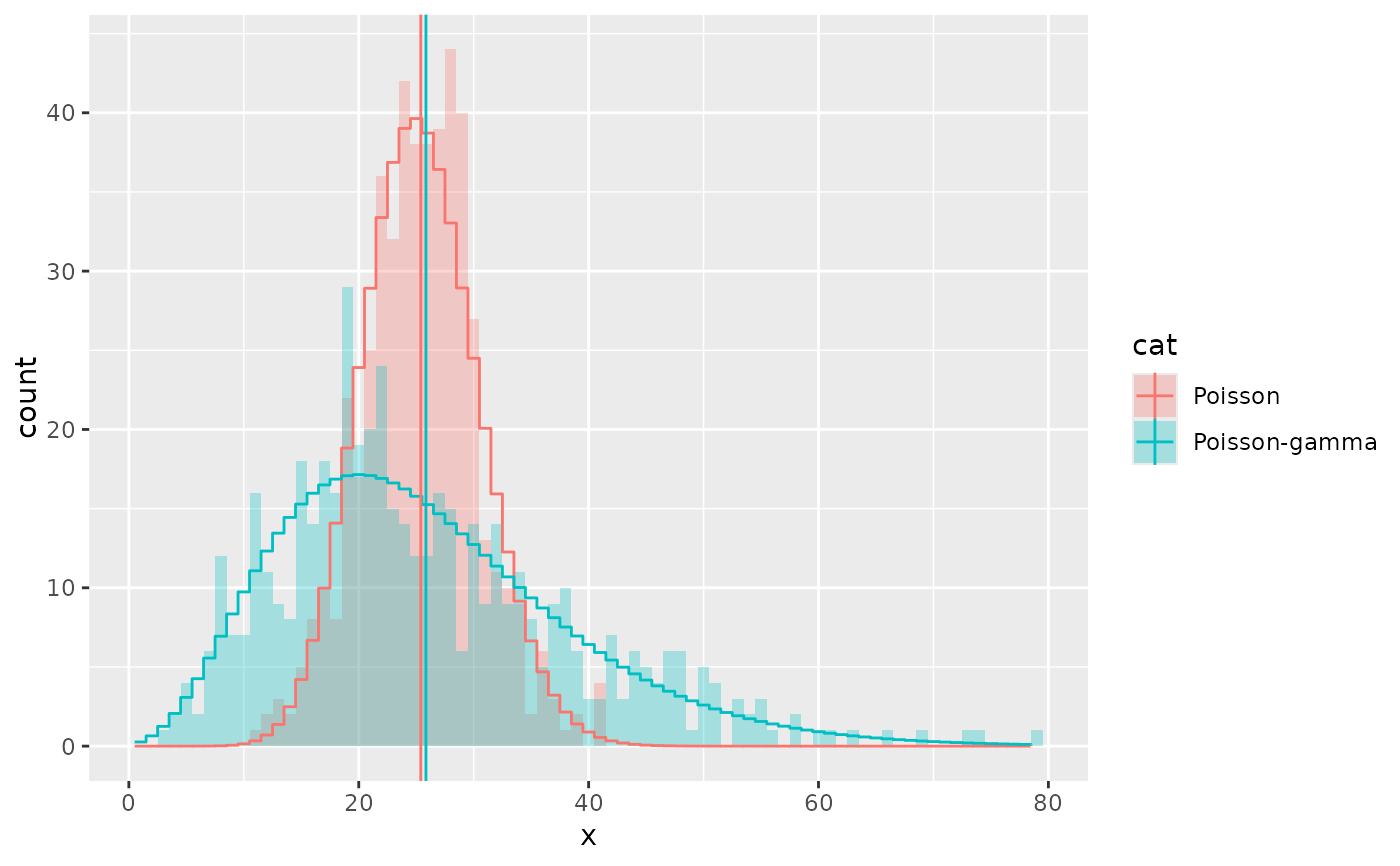
 # A negative binomial can be understood as a Poisson-gamma mixture
df <- data.frame(x = c(rpois(500, 25),
rpois(500, rgamma(500, 5, 0.2))),
cat = rep(c("Poisson", "Poisson-gamma"), each = 500))
ggplot(df, aes(x)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, aes(fill = cat),
alpha = 0.3, position = "identity") +
stat_theodensity(aes(y = stat(count), colour = cat), distri = "nbinom",
geom = "step", position = position_nudge(x = -0.5)) +
stat_summary(aes(y = x, colour = cat, x = 1),
fun.data = function(x){data.frame(xintercept = mean(x))},
geom = "vline")
# A negative binomial can be understood as a Poisson-gamma mixture
df <- data.frame(x = c(rpois(500, 25),
rpois(500, rgamma(500, 5, 0.2))),
cat = rep(c("Poisson", "Poisson-gamma"), each = 500))
ggplot(df, aes(x)) +
geom_histogram(binwidth = 1, aes(fill = cat),
alpha = 0.3, position = "identity") +
stat_theodensity(aes(y = stat(count), colour = cat), distri = "nbinom",
geom = "step", position = position_nudge(x = -0.5)) +
stat_summary(aes(y = x, colour = cat, x = 1),
fun.data = function(x){data.frame(xintercept = mean(x))},
geom = "vline")