Statistical Power for the Generic Z-Test
generic.z.test.RdCalculates power for the generic Z-Test with (optional) Type 1 and Type 2 error plots.
power.z.test(mean = NULL, sd = 1, null.mean = 0, null.sd = 1,
alpha = 0.05, alternative = c("two.sided",
"one.sided", "two.one.sided"),
plot = TRUE, verbose = TRUE, pretty = FALSE, ...)Arguments
- mean
mean of the alternative.
- sd
standard deviation of the alternative. Do not change this value except when some sort of variance correction is applied (e.g. as in logistic and Poisson regressions).
- null.mean
mean of the null. When alternative = "two.one.sided", the function expects two values in the form c(lower, upper). If a single value is provided, it is interpreted as the absolute bound and automatically expanded to c(-value, +value).
- null.sd
standard deviation of the null. Do not change this value except when some sort of correction is applied.
- alpha
type 1 error rate, defined as the probability of incorrectly rejecting a true null hypothesis, denoted as \(\alpha\).
- alternative
character; direction or type of the hypothesis test: "one.sided", "two.sided", or "two.one.sided". "two.one.sided" is used for equivalence and minimal effect testing.
- plot
logical;
FALSEswitches off Type 1 and Type 2 error plot.TRUEby default.- verbose
logical; whether the output should be printed on the console.
TRUEby default.- ...
legacy inputs will be mapped to their corresponding arguments (silent). e.g.
ncp- pretty
logical; whether the output should show Unicode characters (if encoding allows for it).
FALSEby default.
Value
- mean
mean of the alternative distribution.
- sd
standard deviation of the alternative distribution.
- null.mean
mean of the null distribution.
- null.sd
standard deviation of the null distribution.
- z.alpha
critical value(s).
- power
statistical power \((1-\beta)\).
Examples
# two-sided
# power defined as the probability of observing z-statistics
# greater than the positive critical t value OR
# less than the negative critical t value
power.z.test(mean = 1.96, alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "two.sided")
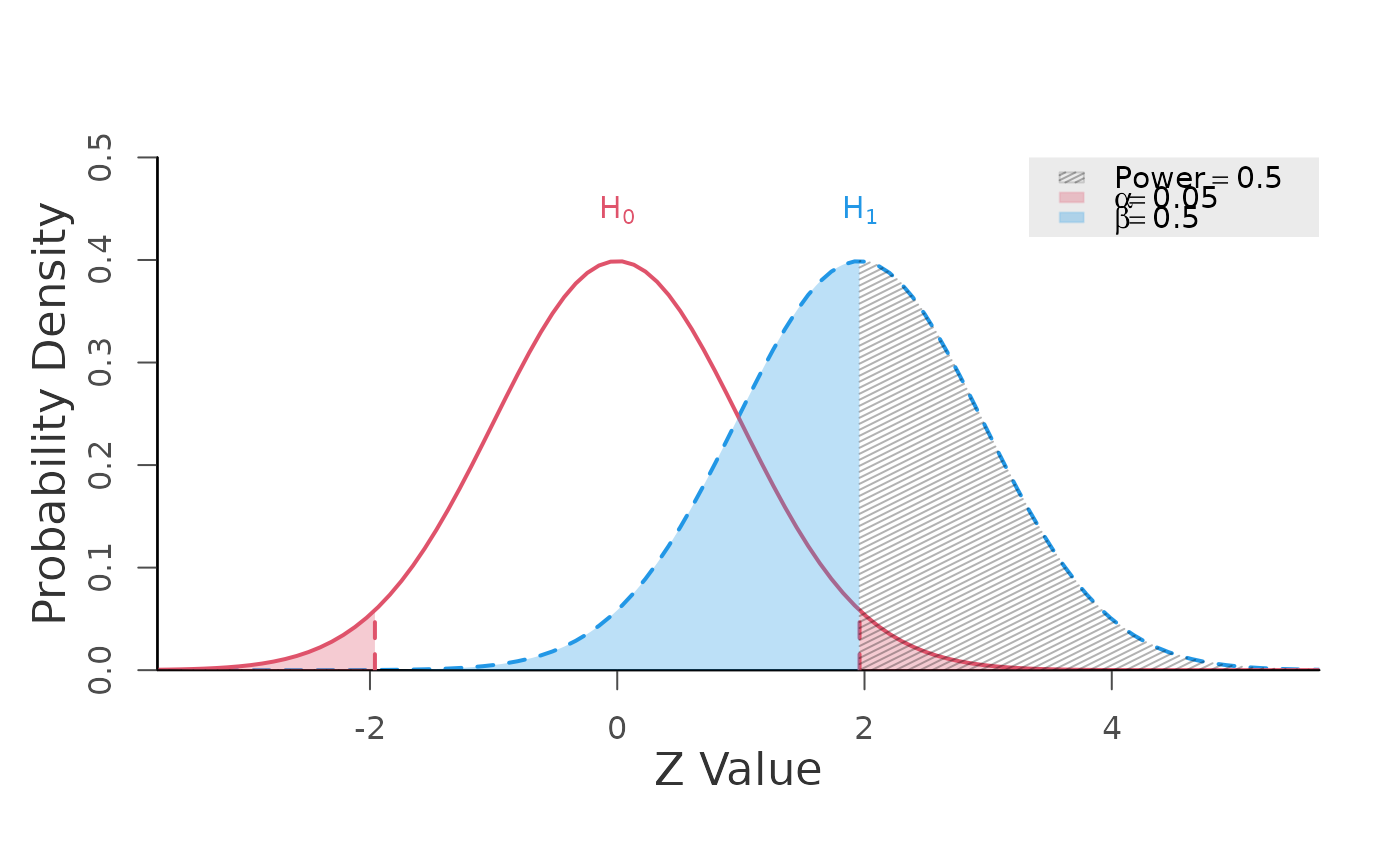 #> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean = null.mean
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean != null.mean
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.500
#> Statistical Power = 0.5 <<
#>
# one-sided
# power is defined as the probability of observing z-statistics
# greater than the critical t value
power.z.test(mean = 1.96, alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "one.sided")
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean = null.mean
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean != null.mean
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.500
#> Statistical Power = 0.5 <<
#>
# one-sided
# power is defined as the probability of observing z-statistics
# greater than the critical t value
power.z.test(mean = 1.96, alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "one.sided")
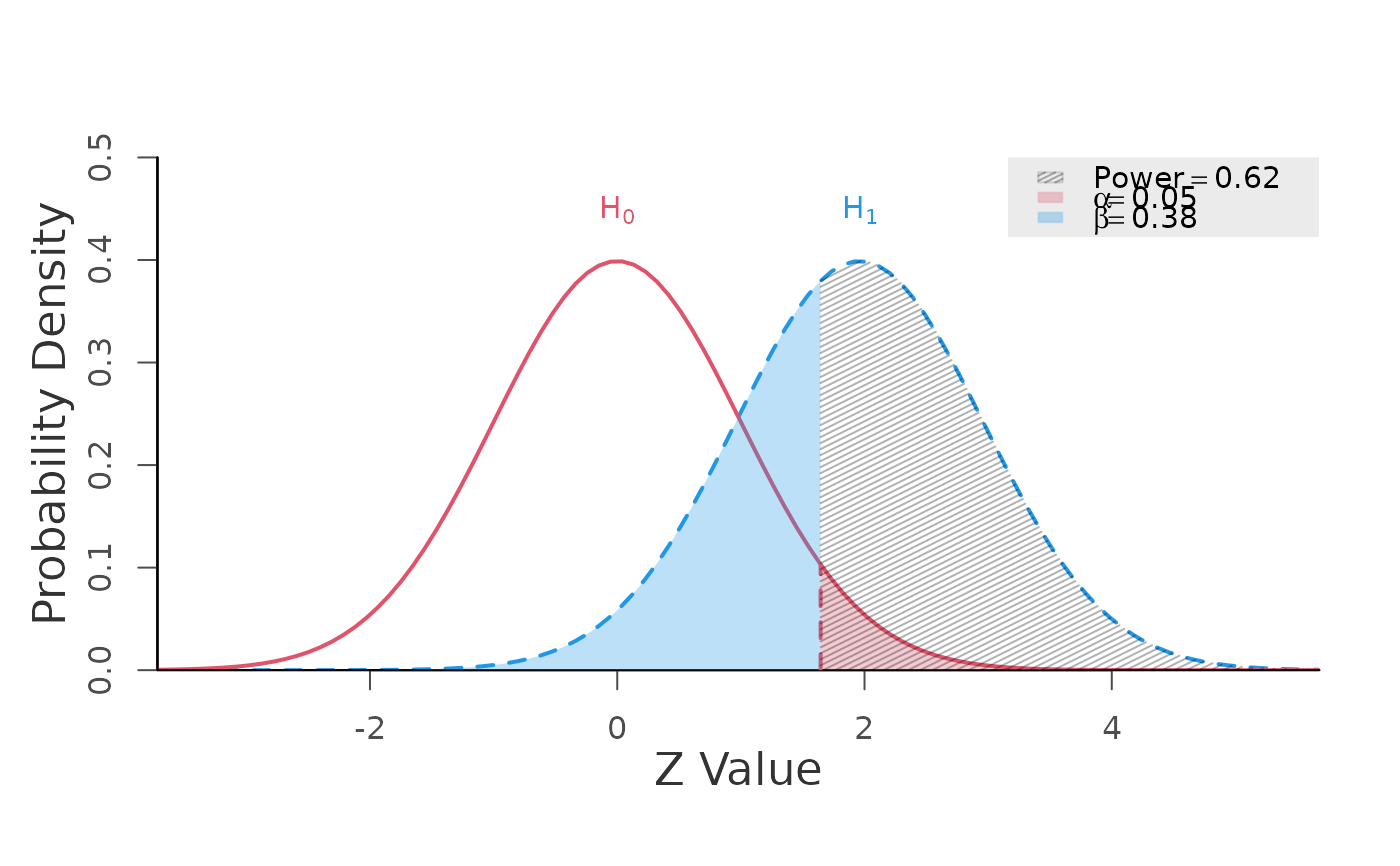 #> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean <= null.mean
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean > null.mean
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.376
#> Statistical Power = 0.624 <<
#>
# equivalence
# power is defined as the probability of observing a test statistic
# greater than the upper critical value (for the lower bound) AND
# less than the lower critical value (for the upper bound)
power.z.test(mean = 0, null.mean = c(-2, 2), alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "two.one.sided")
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean <= null.mean
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean > null.mean
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.376
#> Statistical Power = 0.624 <<
#>
# equivalence
# power is defined as the probability of observing a test statistic
# greater than the upper critical value (for the lower bound) AND
# less than the lower critical value (for the upper bound)
power.z.test(mean = 0, null.mean = c(-2, 2), alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "two.one.sided")
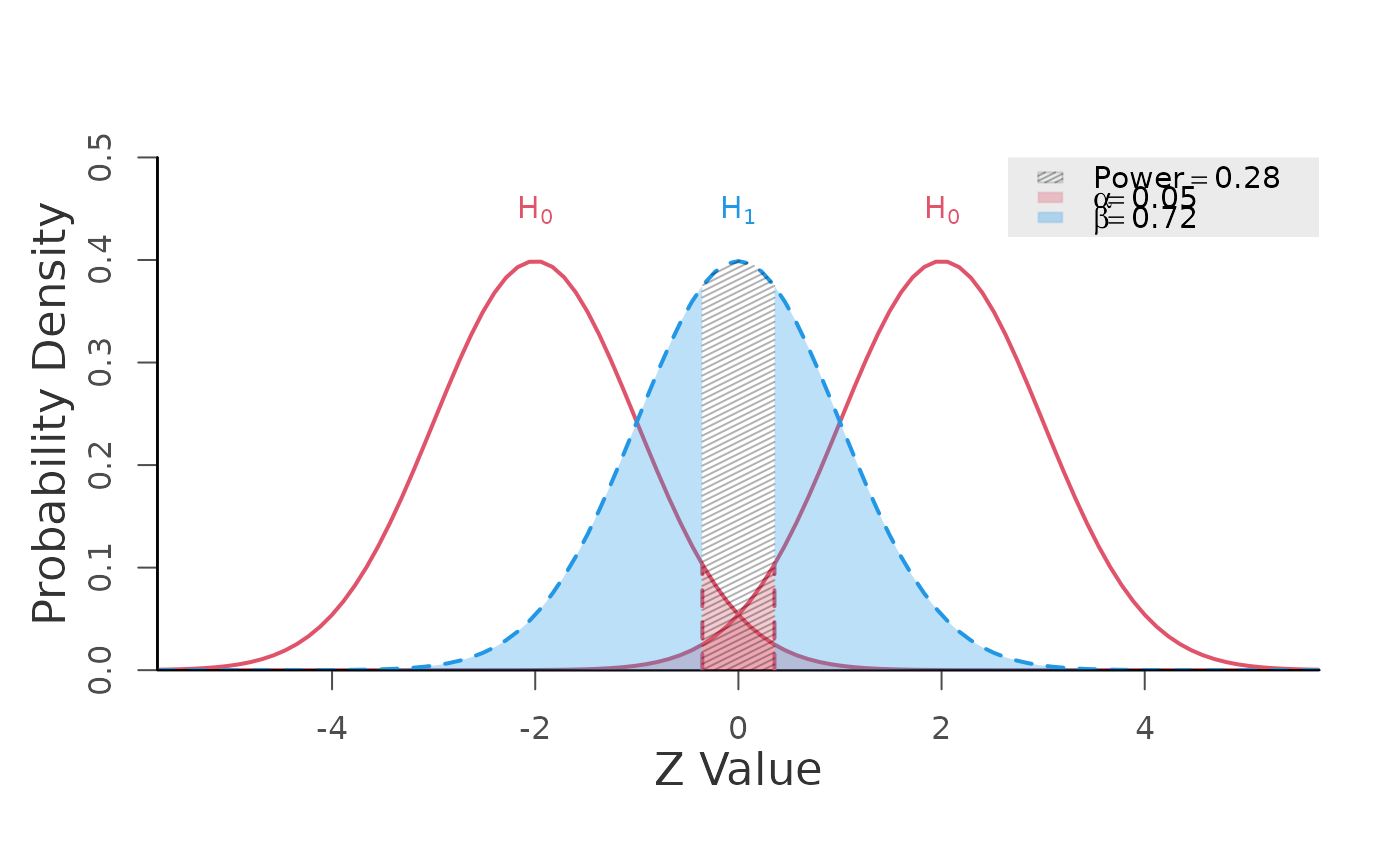 #> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean <= min(null.mean) or
#> mean >= max(null.mean)
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean > min(null.mean) and
#> mean < max(null.mean)
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.722
#> Statistical Power = 0.278 <<
#>
# minimal effect testing
# power is defined as the probability of observing a test statistic
# greater than the upper critical value (for the upper bound) OR
# less than the lower critical value (for the lower bound).
power.z.test(mean = 2, null.mean = c(-1, 1), alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "two.one.sided")
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean <= min(null.mean) or
#> mean >= max(null.mean)
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean > min(null.mean) and
#> mean < max(null.mean)
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.722
#> Statistical Power = 0.278 <<
#>
# minimal effect testing
# power is defined as the probability of observing a test statistic
# greater than the upper critical value (for the upper bound) OR
# less than the lower critical value (for the lower bound).
power.z.test(mean = 2, null.mean = c(-1, 1), alpha = 0.05,
alternative = "two.one.sided")
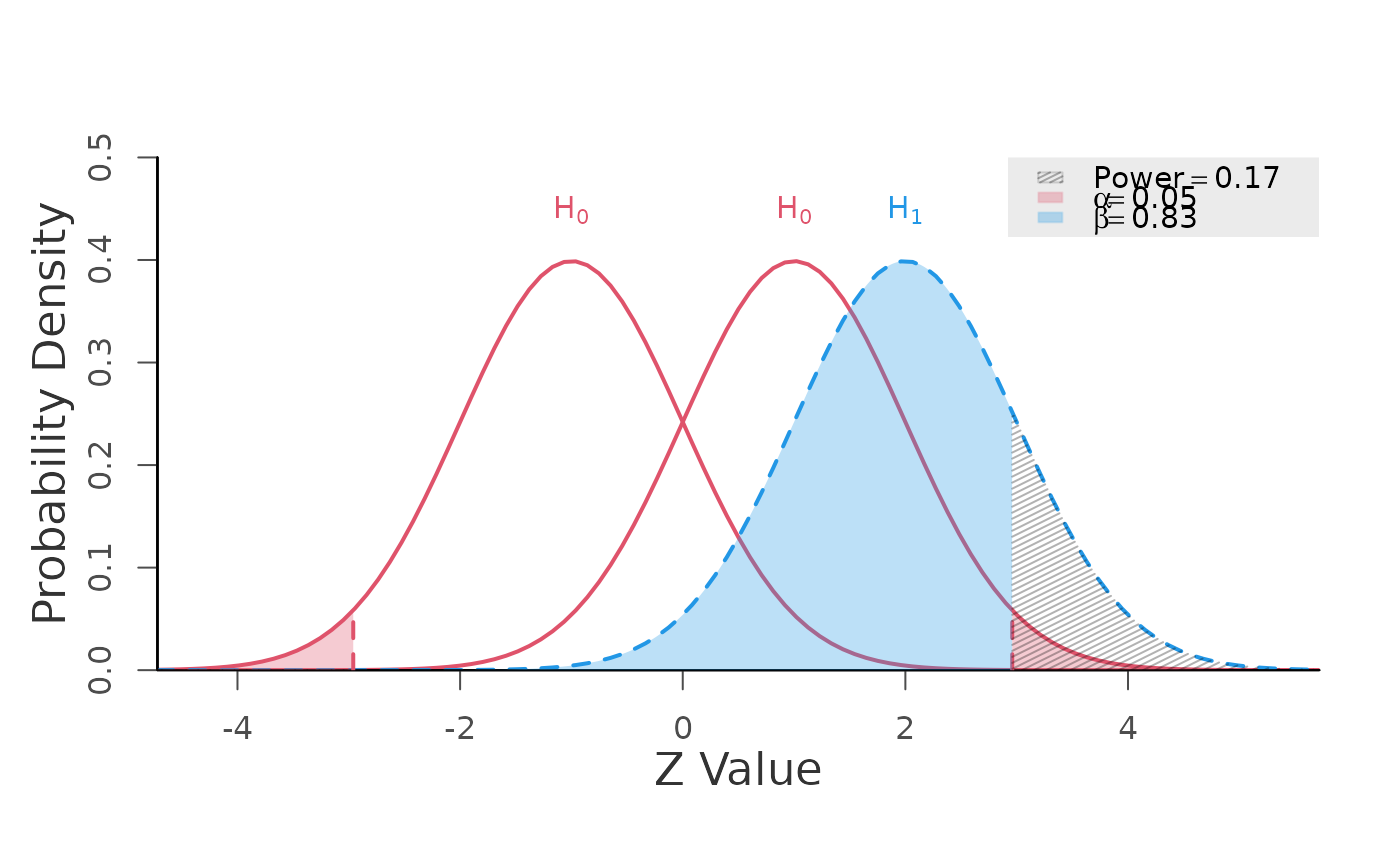 #> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean >= min(null.mean) and
#> mean <= max(null.mean)
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean < min(null.mean) or
#> mean > max(null.mean)
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.831
#> Statistical Power = 0.169 <<
#>
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#> | POWER CALCULATION |
#> +--------------------------------------------------+
#>
#> Generic Z-Test
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Hypotheses
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> H0 (Null Claim) : mean >= min(null.mean) and
#> mean <= max(null.mean)
#> H1 (Alt. Claim) : mean < min(null.mean) or
#> mean > max(null.mean)
#>
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Results
#> ---------------------------------------------------
#> Type 1 Error (alpha) = 0.050
#> Type 2 Error (beta) = 0.831
#> Statistical Power = 0.169 <<
#>