3-D Plots Showing Effects of Two Continuous Predictors in a Regression Model Fit
bplot.RdUses lattice graphics and the output from Predict to plot image,
contour, or perspective plots showing the simultaneous effects of two
continuous predictor variables. Unless formula is provided, the
\(x\)-axis is constructed from the first variable listed in the call
to Predict and the \(y\)-axis variable comes from the second.
The perimeter function is used to generate the boundary of data
to plot when a 3-d plot is made. It finds the area where there are
sufficient data to generate believable interaction fits.
Arguments
- x
for
bplot, an object created byPredictfor which two or more numeric predictors varied. Forperimis the first variable of a pair of predictors forming a 3-d plot.- formula
a formula of the form
f(yhat) ~ x*yoptionally followed by |a*b*c which are 1-3 paneling variables that were specified toPredict.fcan represent any R function of a vector that produces a vector. If the left hand side of the formula is omitted,yhatwill be inserted. Ifformulais omitted, it will be inferred from the first two variables that varied in the call toPredict.- lfun
a high-level lattice plotting function that takes formulas of the form
z ~ x*y. The default is an image plot (levelplot). Other common choices arewireframefor perspective plot orcontourplotfor a contour plot.- xlab
Character string label for \(x\)-axis. Default is given by
Predict.- ylab
Character string abel for \(y\)-axis
- zlab
Character string \(z\)-axis label for perspective (wireframe) plots. Default comes from
Predict.zlabwill often be specified iffunwas specified toPredict.- adj.subtitle
Set to
FALSEto suppress subtitling the graph with the list of settings of non-graphed adjustment values. Default isTRUEif there are non-plotted adjustment variables andref.zerowas not used.- cex.adj
cexparameter for size of adjustment settings in subtitles. Default is 0.75- cex.lab
cexparameter for axis labels. Default is 1.- perim
names a matrix created by
perimeterwhen used for 3-d plots of two continuous predictors. When the combination of variables is outside the range inperim, that section of the plot is suppressed. Ifperimis omitted, 3-d plotting will use the marginal distributions of the two predictors to determine the plotting region, when the grid is not specified explicitly invariables. When instead a series of curves is being plotted,perimspecifies a function having two arguments. The first is the vector of values of the first variable that is about to be plotted on the \(x\)-axis. The second argument is the single value of the variable representing different curves, for the current curve being plotted. The function's returned value must be a logical vector whose length is the same as that of the first argument, with valuesTRUEif the corresponding point should be plotted for the current curve,FALSEotherwise. See one of the latter examples.- showperim
set to
TRUEifperimis specified and you want to show the actual perimeter used.- zlim
Controls the range for plotting in the \(z\)-axis if there is one. Computed by default.
- scales
see
wireframe- xlabrot
rotation angle for the x-axis. Default is 30 for
wireframeand 0 otherwise.- ylabrot
rotation angle for the y-axis. Default is -40 for
wireframe, 90 forcontourplotorlevelplot, and 0 otherwise.- zlabrot
rotation angle for z-axis rotation for
wireframeplots- ...
other arguments to pass to the lattice function
- y
second variable of the pair for
perim. If omitted,xis assumed to be a list with bothxandycomponents.- xinc
increment in
xover which to examine the density ofyinperimeter- n
within intervals of
xforperimeter, takes the informative range ofyto be the \(n\)th smallest to the \(n\)th largest values ofy. If there aren't at least 2\(n\)yvalues in thexinterval, noyranges are used for that interval.- lowess.
set to
FALSEto not havelowesssmooth the data perimeters
Value
perimeter returns a matrix of class perimeter. This
outline can be conveniently plotted by lines.perimeter.
Details
perimeter is a kind of generalization of datadist for 2
continuous variables. First, the n smallest and largest x
values are determined. These form the lowest and highest possible
xs to display. Then x is grouped into intervals bounded
by these two numbers, with the interval widths defined by xinc.
Within each interval, y is sorted and the \(n\)th smallest and
largest y are taken as the interval containing sufficient data
density to plot interaction surfaces. The interval is ignored when
there are insufficient y values. When the data are being
readied for persp, bplot uses the approx function to do
linear interpolation of the y-boundaries as a function of the
x values actually used in forming the grid (the values of the
first variable specified to Predict). To make the perimeter smooth,
specify lowess.=TRUE to perimeter.
Examples
n <- 1000 # define sample size
set.seed(17) # so can reproduce the results
age <- rnorm(n, 50, 10)
blood.pressure <- rnorm(n, 120, 15)
cholesterol <- rnorm(n, 200, 25)
sex <- factor(sample(c('female','male'), n,TRUE))
label(age) <- 'Age' # label is in Hmisc
label(cholesterol) <- 'Total Cholesterol'
label(blood.pressure) <- 'Systolic Blood Pressure'
label(sex) <- 'Sex'
units(cholesterol) <- 'mg/dl' # uses units.default in Hmisc
units(blood.pressure) <- 'mmHg'
# Specify population model for log odds that Y=1
L <- .4*(sex=='male') + .045*(age-50) +
(log(cholesterol - 10)-5.2)*(-2*(sex=='female') + 2*(sex=='male'))
# Simulate binary y to have Prob(y=1) = 1/[1+exp(-L)]
y <- ifelse(runif(n) < plogis(L), 1, 0)
ddist <- datadist(age, blood.pressure, cholesterol, sex)
options(datadist='ddist')
fit <- lrm(y ~ blood.pressure + sex * (age + rcs(cholesterol,4)),
x=TRUE, y=TRUE)
#> Error in Design(data, formula = formula): dataset ddist not found for options(datadist=)
p <- Predict(fit, age, cholesterol, sex, np=50) # vary sex last
#> Error: object 'fit' not found
require(lattice)
bplot(p) # image plot for age, cholesterol with color
#> Error: object 'p' not found
# coming from yhat; use default ranges for
# both continuous predictors; two panels (for sex)
bplot(p, lfun=wireframe) # same as bplot(p,,wireframe)
#> Error: object 'p' not found
# View from different angle, change y label orientation accordingly
# Default is z=40, x=-60
bplot(p,, wireframe, screen=list(z=40, x=-75), ylabrot=-25)
#> Error: object 'p' not found
bplot(p,, contourplot) # contour plot
#> Error: object 'p' not found
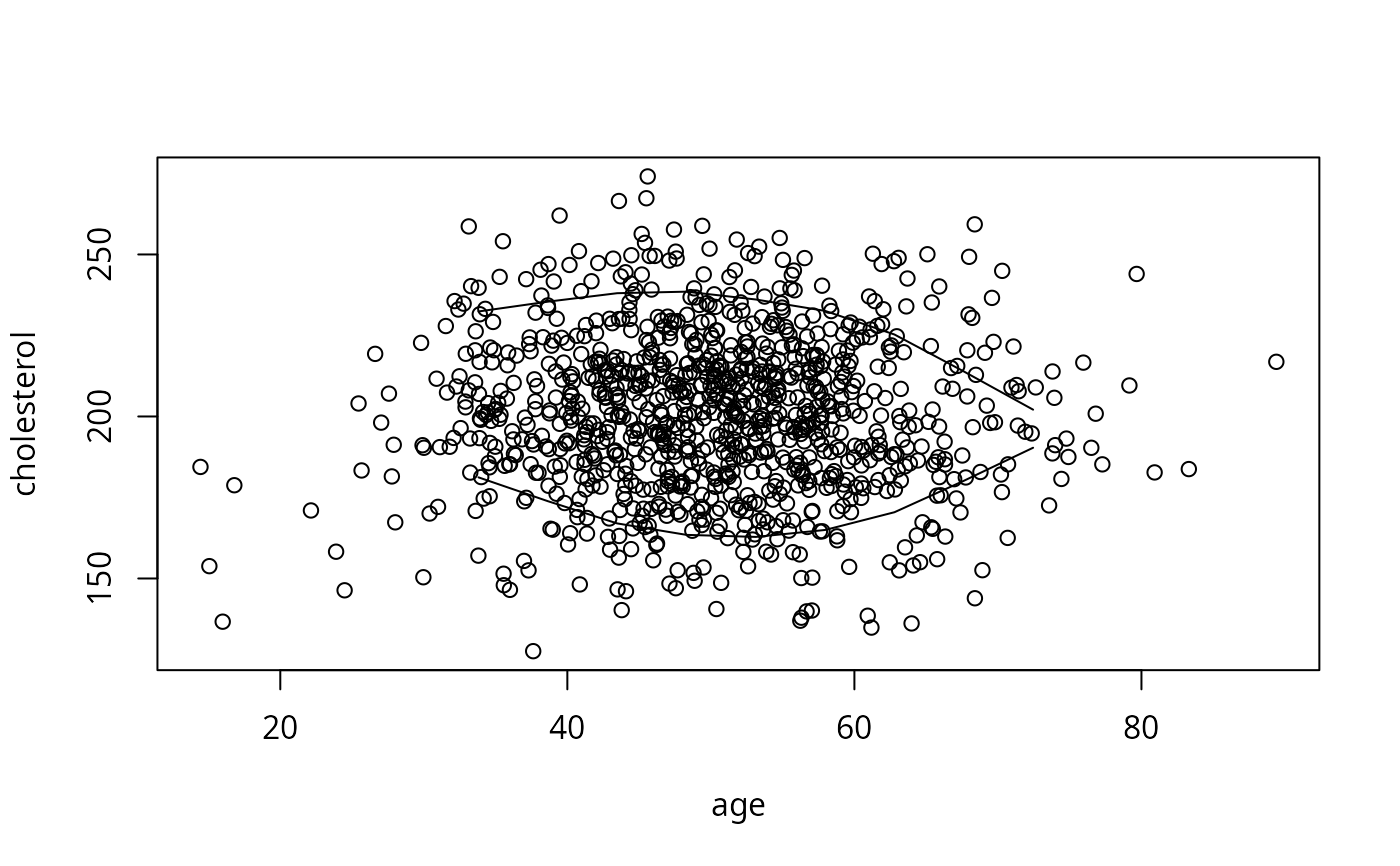
bounds <- perimeter(age, cholesterol, lowess=TRUE)
plot(age, cholesterol) # show bivariate data density and perimeter
lines(bounds[,c('x','ymin')]); lines(bounds[,c('x','ymax')])
 p <- Predict(fit, age, cholesterol) # use only one sex
#> Error: object 'fit' not found
bplot(p, perim=bounds) # draws image() plot
#> Error: object 'p' not found
# don't show estimates where data are sparse
# doesn't make sense here since vars don't interact
bplot(p, plogis(yhat) ~ age*cholesterol) # Probability scale
#> Error: object 'p' not found
options(datadist=NULL)
p <- Predict(fit, age, cholesterol) # use only one sex
#> Error: object 'fit' not found
bplot(p, perim=bounds) # draws image() plot
#> Error: object 'p' not found
# don't show estimates where data are sparse
# doesn't make sense here since vars don't interact
bplot(p, plogis(yhat) ~ age*cholesterol) # Probability scale
#> Error: object 'p' not found
options(datadist=NULL)