Take a regular sample
sample.RdTake a spatial sample from a SpatRaster, SpatVector or SpatExtent. Sampling a SpatVector or SpatExtent always returns a SpatVector of points.
With a SpatRaster, you can get cell values, cell numbers (cells=TRUE), coordinates (xy=TRUE) or (when method="regular" and as.raster=TRUE) get a new SpatRaster with the same extent, but fewer cells.
In order to assure regularity when requesting a regular sample, the number of cells or points returned may not be exactly the same as the size requested unless you use exact=TRUE.
# S4 method for class 'SpatRaster'
spatSample(x, size, method="random", replace=FALSE, na.rm=FALSE,
as.raster=FALSE, as.df=TRUE, as.points=FALSE, values=hasValues(x), cells=FALSE,
xy=FALSE, ext=NULL, warn=TRUE, weights=NULL, exp=5, exhaustive=FALSE,
exact=FALSE, each=TRUE, ...)
# S4 method for class 'SpatVector'
spatSample(x, size, method="random", strata=NULL, chess="")
# S4 method for class 'SpatExtent'
spatSample(x, size, method="random", lonlat, as.points=FALSE, exact=FALSE)Arguments
- x
SpatRaster, SpatVector or SpatExtent
- size
numeric. The sample size. If
xis a SpatVector, you can also provide a vector of the same length asxin which case sampling is done separately for each geometry. Ifxis a SpatRaster, and you are usingmethod="regular"you can specify the size as two numbers (number of rows and columns). Note that when usingmethod="stratified", the sample size is returned for each stratum- method
character. Should be "regular" or "random", If
xis aSpatRaster, it can also be "stratified" (each value inxis a stratum), "weights" (each value inxis a probability weight), or "spread" (an approximately regular sample, using compact zones generated withk_meansclustering of the raster cell locations)- replace
logical. If
TRUE, sampling is with replacement (ifmethod="random")- na.rm
logical. If
TRUE,NAsare removed. Only used with random sampling of cell values. That is withmethod="random", as.raster=FALSE, cells=FALSE- as.raster
logical. If
TRUE, a SpatRaster is returned- as.df
logical. If
TRUE, a data.frame is returned instead of a matrix- as.points
logical. If
TRUE, a SpatVector of points is returned- values
logical. If
TRUEraster cell values are returned- cells
logical. If
TRUE, cell numbers are returned. Ifmethod="stratified"this is always set toTRUEifxy=FALSE- xy
logical. If
TRUE, cell coordinates are returned- ext
SpatExtent or NULL to restrict sampling to a subset of the area of
x- warn
logical. Give a warning if the sample size returned is smaller than requested
- weights
SpatRaster. Used to provide weights when
method="stratified"- lonlat
logical. If
TRUE, sampling of a SpatExtent is weighted bycos(latitude). For SpatRaster and SpatVector this done based on thecrs, but it is ignored ifas.raster=TRUE- exp
numeric >= 1. "Expansion factor" that is multiplied with
sizeto get an initial sample used for stratified samples and random samples withna.rm=TRUEto try to get at leastsizesamples- exhaustive
logical. If
TRUEand (method=="random"andna.rm=TRUE) ormethod=="stratified", all cells that are notNAare determined and a sample is taken from these cells. This is useful when you are dealing with a very large raster that is sparse (most cells areNA). Otherwise, the default approach may not find enough samples. This should not be used in other cases, especially not with large rasters that mostly have values- exact
logical. If
TRUEandmethod=="regular", the sample returned is exactlysize, perhaps at the expense of some regularity. Otherwise you get at leastsizemany samples. Ignored for lon/lat rasters- each
logical. If
TRUEandmethod=="stratified", the sample returned issizefor each stratum. Otherwisesizeis the total sample size- ...
additional arguments passed to
k_meanswhenmethod="kmeans"- strata
if not NULL, stratified random sampling is done, taking
sizesamples from each stratum. Ifxhas polygon geometry,stratamust be a field name (or index) inx. Ifxhas point geometry,stratacan be a SpatVector of polygons or a SpatRaster- chess
character. One of "", "white", or "black". For stratified sampling if
stratais a SpatRaster. If not "", samples are only taken from alternate cells, organized like the "white" or "black" fields on a chessboard
Value
numeric matrix, data.frame, SpatRaster or SpatVector
Examples
f <- system.file("ex/elev.tif", package="terra")
r <- rast(f)
s <- spatSample(r, 10, as.raster=TRUE)
spatSample(r, 5)
#> elevation
#> 1 380
#> 2 NA
#> 3 495
#> 4 413
#> 5 341
spatSample(r, 5, na.rm=TRUE)
#> elevation
#> 1 250
#> 2 260
#> 3 332
#> 4 462
#> 5 318
spatSample(r, 5, "regular")
#> elevation
#> 1 479
#> 2 NaN
#> 3 NaN
#> 4 419
#> 5 290
#> 6 306
#> 7 281
#> 8 286
#> 9 NaN
## if you require cell numbers and/or coordinates
size <- 6
spatSample(r, 6, "random", cells=TRUE, xy=TRUE, values=FALSE)
#> cell x y
#> [1,] 5743 6.095833 49.68750
#> [2,] 3037 6.504167 49.92917
#> [3,] 5898 5.804167 49.67083
#> [4,] 7943 6.220833 49.49583
#> [5,] 2926 6.370833 49.93750
#> [6,] 2015 5.904167 50.01250
# regular, with values
spatSample(r, 6, "regular", cells=TRUE, xy=TRUE)
#> cell x y elevation
#> 1 7458 6.137500 49.53750 264
#> 2 7505 6.529167 49.53750 NA
#> 3 7411 5.745833 49.53750 NA
#> 4 5368 6.137500 49.72083 289
#> 5 5415 6.529167 49.72083 NA
#> 6 5321 5.745833 49.72083 NA
#> 7 3183 6.137500 49.91250 322
#> 8 1093 6.137500 50.09583 NA
# stratified
rr <- rast(ncol=10, nrow=10, names="stratum")
set.seed(1)
values(rr) <- round(runif(ncell(rr), 1, 3))
spatSample(rr, 2, "stratified", xy=TRUE)
#> x y stratum
#> [1,] -162 -81 1
#> [2,] -54 45 1
#> [3,] -126 -27 2
#> [4,] 90 -81 2
#> [5,] -162 9 3
#> [6,] 54 27 3
s <- spatSample(rr, 5, "stratified", as.points=TRUE, each=FALSE)
plot(rr, plg=list(title="raster"))
plot(s, 1, add=TRUE, plg=list(x=185, y=1, title="points"), col=rainbow(5))
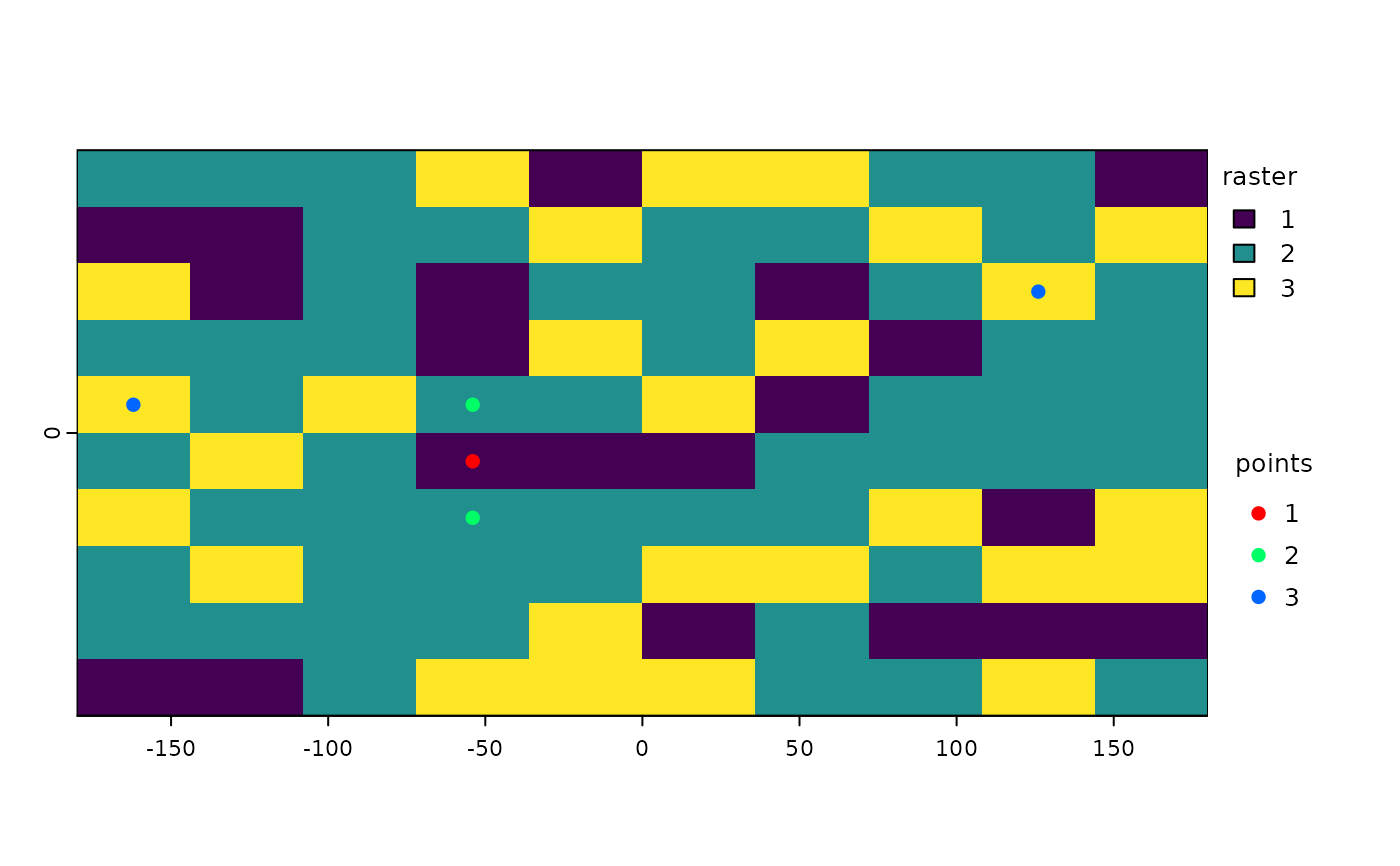 # spread
s <- spatSample(r, 10, "spread", as.points=TRUE)
plot(r); points(s)
# spread
s <- spatSample(r, 10, "spread", as.points=TRUE)
plot(r); points(s)
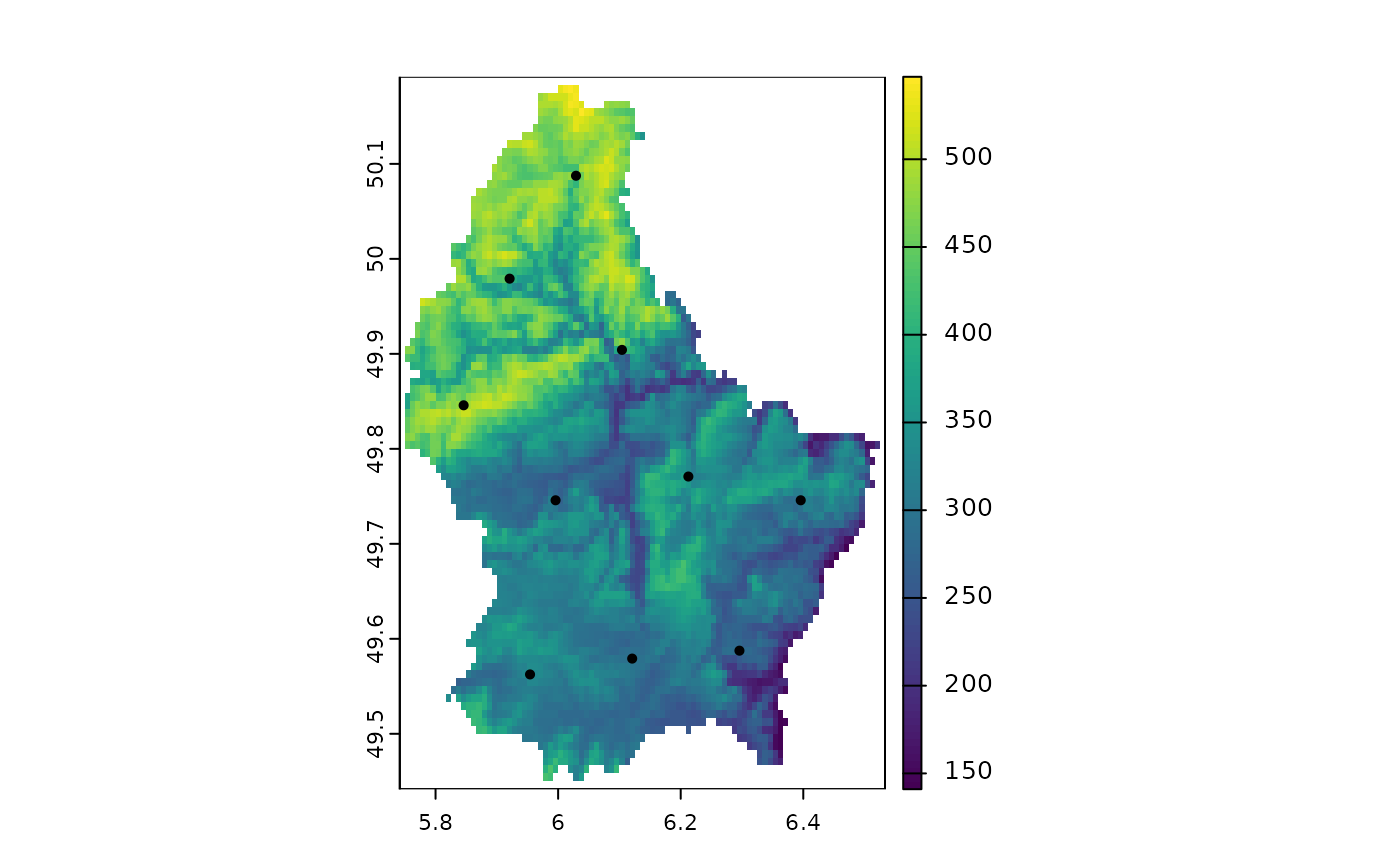 ## SpatExtent
e <- ext(r)
spatSample(e, 10, "random", lonlat=TRUE)
#> x y
#> [1,] 6.060745 49.45733
#> [2,] 6.389876 49.58025
#> [3,] 6.345150 50.02372
#> [4,] 5.901934 50.08592
#> [5,] 6.307978 49.52574
#> [6,] 6.234556 49.74633
#> [7,] 6.037959 50.11587
#> [8,] 5.892183 49.49884
#> [9,] 5.856140 49.48130
#> [10,] 6.134349 49.84738
## SpatVector
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
# sample the geometries
i <- sample(v, 3)
# sample points in geometries
p <- spatSample(v, 3)
## SpatExtent
e <- ext(r)
spatSample(e, 10, "random", lonlat=TRUE)
#> x y
#> [1,] 6.060745 49.45733
#> [2,] 6.389876 49.58025
#> [3,] 6.345150 50.02372
#> [4,] 5.901934 50.08592
#> [5,] 6.307978 49.52574
#> [6,] 6.234556 49.74633
#> [7,] 6.037959 50.11587
#> [8,] 5.892183 49.49884
#> [9,] 5.856140 49.48130
#> [10,] 6.134349 49.84738
## SpatVector
f <- system.file("ex/lux.shp", package="terra")
v <- vect(f)
# sample the geometries
i <- sample(v, 3)
# sample points in geometries
p <- spatSample(v, 3)