Logit Link Function
logitlink.RdComputes the logit transformation, including its inverse and the first nine derivatives.
logitlink(theta, bvalue = NULL, inverse = FALSE, deriv = 0,
short = TRUE, tag = FALSE)
extlogitlink(theta, min = 0, max = 1, bminvalue = NULL,
bmaxvalue = NULL, inverse = FALSE, deriv = 0,
short = TRUE, tag = FALSE)Arguments
- theta
Numeric or character. See below for further details.
- bvalue, bminvalue, bmaxvalue
See
Links. These are boundary values. Forextlogitlink, values ofthetaless than or equal to \(A\) or greater than or equal to \(B\) can be replaced bybminvalueandbmaxvalue.
- min, max
For
extlogitlink,mingives \(A\),maxgives \(B\), and for out of range values,bminvalueandbmaxvalue.- inverse, deriv, short, tag
Details at
Links.
Details
The logit link function is very commonly used for parameters
that lie in the unit interval.
It is the inverse CDF of the logistic distribution.
Numerical values of theta close to 0 or 1 or out of range
result in
Inf, -Inf, NA or NaN.
The extended logit link function extlogitlink
should be used more generally for parameters that lie in the
interval \((A,B)\), say.
The formula is
$$\log((\theta-A)/(B-\theta))$$
and the default values for \(A\) and \(B\) correspond to
the ordinary logit function.
Numerical values of theta close to \(A\)
or \(B\) or out of range result in
Inf, -Inf, NA or NaN.
However these can be replaced by values \(bminvalue\) and
\(bmaxvalue\) first before computing the link function.
Value
For logitlink with deriv = 0, the logit
of theta, i.e., log(theta/(1-theta)) when
inverse = FALSE, and if inverse = TRUE then
exp(theta)/(1+exp(theta)).
For deriv = 1, then the function returns
d eta / d theta as a function of
theta if inverse = FALSE,
else if inverse = TRUE then it returns the reciprocal.
Here, all logarithms are natural logarithms, i.e., to base e.
References
McCullagh, P. and Nelder, J. A. (1989). Generalized Linear Models, 2nd ed. London: Chapman & Hall.
Note
Numerical instability may occur when theta is
close to 1 or 0 (for logitlink), or close to \(A\)
or \(B\) for extlogitlink.
One way of overcoming this is to use, e.g., bvalue.
In terms of the threshold approach with cumulative probabilities
for an ordinal response this link function corresponds to the
univariate logistic distribution (see logistic).
See also
Examples
p <- seq(0.01, 0.99, by = 0.01)
logitlink(p)
#> [1] -4.59511985 -3.89182030 -3.47609869 -3.17805383 -2.94443898 -2.75153531
#> [7] -2.58668934 -2.44234704 -2.31363493 -2.19722458 -2.09074110 -1.99243016
#> [13] -1.90095876 -1.81528997 -1.73460106 -1.65822808 -1.58562726 -1.51634749
#> [19] -1.45001018 -1.38629436 -1.32492541 -1.26566637 -1.20831121 -1.15267951
#> [25] -1.09861229 -1.04596856 -0.99462258 -0.94446161 -0.89538405 -0.84729786
#> [31] -0.80011930 -0.75377180 -0.70818506 -0.66329422 -0.61903921 -0.57536414
#> [37] -0.53221681 -0.48954823 -0.44731222 -0.40546511 -0.36396538 -0.32277339
#> [43] -0.28185115 -0.24116206 -0.20067070 -0.16034265 -0.12014431 -0.08004271
#> [49] -0.04000533 0.00000000 0.04000533 0.08004271 0.12014431 0.16034265
#> [55] 0.20067070 0.24116206 0.28185115 0.32277339 0.36396538 0.40546511
#> [61] 0.44731222 0.48954823 0.53221681 0.57536414 0.61903921 0.66329422
#> [67] 0.70818506 0.75377180 0.80011930 0.84729786 0.89538405 0.94446161
#> [73] 0.99462258 1.04596856 1.09861229 1.15267951 1.20831121 1.26566637
#> [79] 1.32492541 1.38629436 1.45001018 1.51634749 1.58562726 1.65822808
#> [85] 1.73460106 1.81528997 1.90095876 1.99243016 2.09074110 2.19722458
#> [91] 2.31363493 2.44234704 2.58668934 2.75153531 2.94443898 3.17805383
#> [97] 3.47609869 3.89182030 4.59511985
max(abs(logitlink(logitlink(p), inverse = TRUE) - p)) # 0?
#> [1] 1.110223e-16
p <- c(seq(-0.02, 0.02, by = 0.01), seq(0.97, 1.02, by = 0.01))
logitlink(p) # Has NAs
#> [1] NaN NaN -Inf -4.595120 -3.891820 3.476099 3.891820
#> [8] 4.595120 Inf NaN NaN
logitlink(p, bvalue = .Machine$double.eps) # Has no NAs
#> [1] -36.043653 -36.043653 -36.043653 -4.595120 -3.891820 3.476099
#> [7] 3.891820 4.595120 36.043653 36.043653 36.043653
p <- seq(0.9, 2.2, by = 0.1)
extlogitlink(p, min = 1, max = 2,
bminvalue = 1 + .Machine$double.eps,
bmaxvalue = 2 - .Machine$double.eps) # Has no NAs
#> [1] -36.0436534 -36.0436534 -2.1972246 -1.3862944 -0.8472979 -0.4054651
#> [7] 0.0000000 0.4054651 0.8472979 1.3862944 2.1972246 36.0436534
#> [13] 36.0436534 36.0436534
if (FALSE) par(mfrow = c(2,2), lwd = (mylwd <- 2))
y <- seq(-4, 4, length = 100)
p <- seq(0.01, 0.99, by = 0.01)
for (d in 0:1) {
myinv <- (d > 0)
matplot(p, cbind( logitlink(p, deriv = d, inv = myinv),
probitlink(p, deriv = d, inv = myinv)), las = 1,
type = "n", col = "purple", ylab = "transformation",
main = if (d == 0) "Some probability link functions"
else "1 / first derivative")
lines(p, logitlink(p, deriv = d, inverse = myinv), col = "limegreen")
lines(p, probitlink(p, deriv = d, inverse = myinv), col = "purple")
lines(p, clogloglink(p, deriv = d, inverse = myinv), col = "chocolate")
lines(p, cauchitlink(p, deriv = d, inverse = myinv), col = "tan")
if (d == 0) {
abline(v = 0.5, h = 0, lty = "dashed")
legend(0, 4.5, c("logitlink", "probitlink",
"clogloglink", "cauchitlink"), col = c("limegreen", "purple",
"chocolate", "tan"), lwd = mylwd)
} else
abline(v = 0.5, lty = "dashed")
}
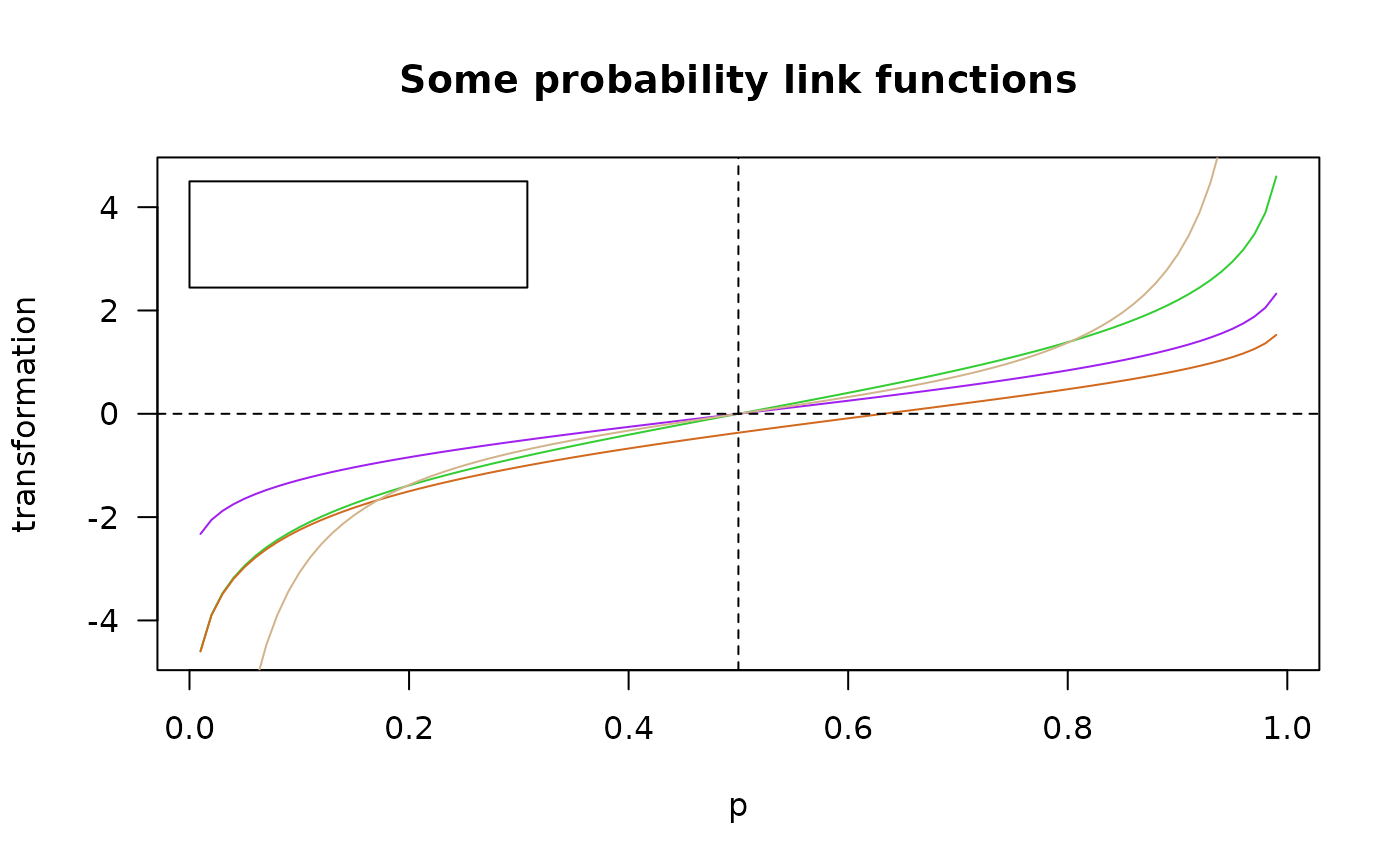 #> Error: object 'mylwd' not found
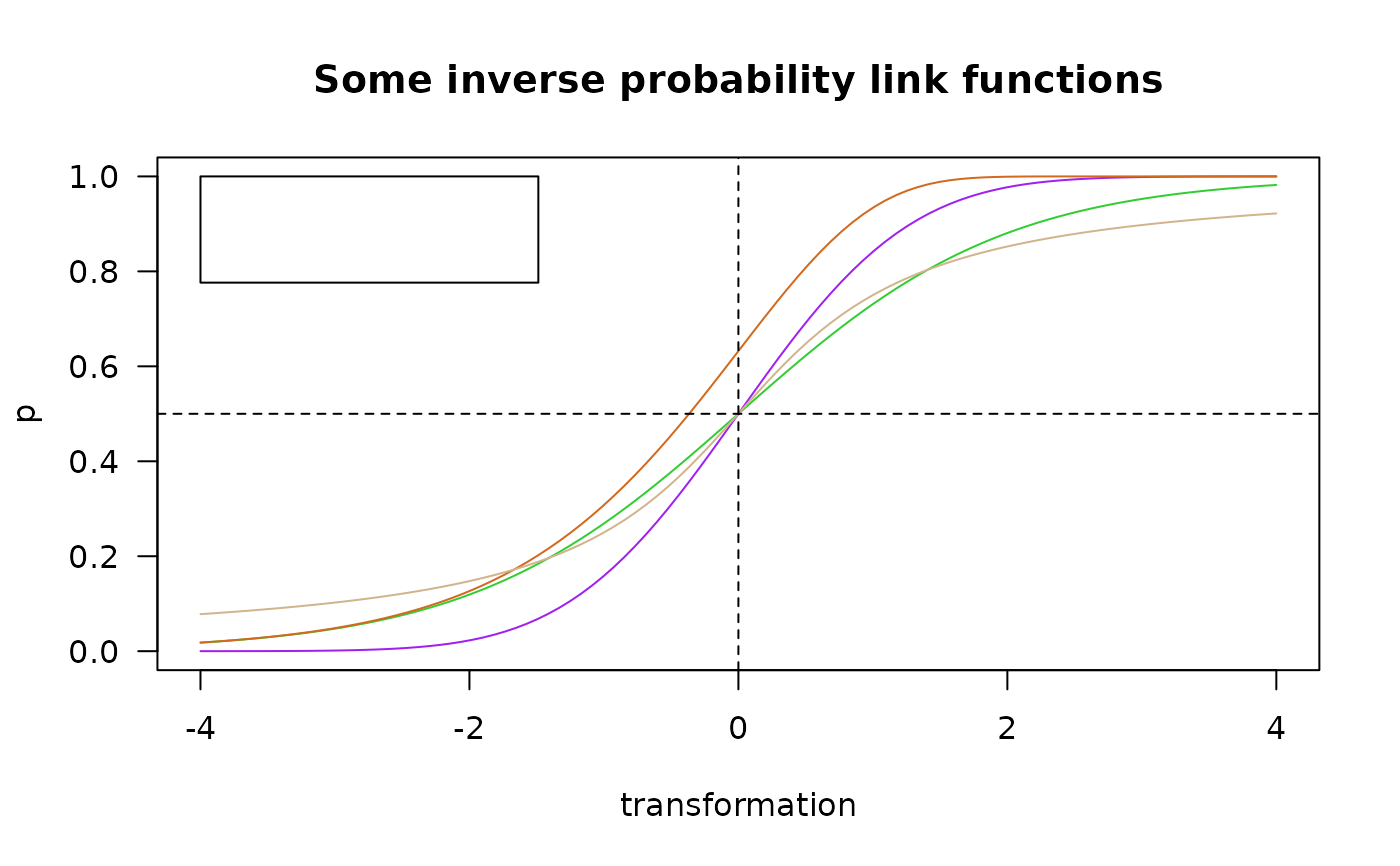
for (d in 0) {
matplot(y, cbind(logitlink(y, deriv = d, inverse = TRUE),
probitlink(y, deriv = d, inverse = TRUE)), las = 1,
type = "n", col = "purple", xlab = "transformation", ylab = "p",
main = if (d == 0) "Some inverse probability link functions"
else "First derivative")
lines(y, logitlink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "limegreen")
lines(y, probitlink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "purple")
lines(y, clogloglink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "chocolate")
lines(y, cauchitlink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "tan")
if (d == 0) {
abline(h = 0.5, v = 0, lty = "dashed")
legend(-4, 1, c("logitlink", "probitlink", "clogloglink",
"cauchitlink"), col = c("limegreen", "purple",
"chocolate", "tan"), lwd = mylwd)
}
}
#> Error: object 'mylwd' not found
for (d in 0) {
matplot(y, cbind(logitlink(y, deriv = d, inverse = TRUE),
probitlink(y, deriv = d, inverse = TRUE)), las = 1,
type = "n", col = "purple", xlab = "transformation", ylab = "p",
main = if (d == 0) "Some inverse probability link functions"
else "First derivative")
lines(y, logitlink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "limegreen")
lines(y, probitlink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "purple")
lines(y, clogloglink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "chocolate")
lines(y, cauchitlink(y, deriv = d, inv = TRUE), col = "tan")
if (d == 0) {
abline(h = 0.5, v = 0, lty = "dashed")
legend(-4, 1, c("logitlink", "probitlink", "clogloglink",
"cauchitlink"), col = c("limegreen", "purple",
"chocolate", "tan"), lwd = mylwd)
}
}
 #> Error: object 'mylwd' not found
p <- seq(0.21, 0.59, by = 0.01)
plot(p, extlogitlink(p, min = 0.2, max = 0.6), xlim = c(0, 1),
type = "l", col = "black", ylab = "transformation",
las = 1, main = "extlogitlink(p, min = 0.2, max = 0.6)")
#> Error: object 'mylwd' not found
p <- seq(0.21, 0.59, by = 0.01)
plot(p, extlogitlink(p, min = 0.2, max = 0.6), xlim = c(0, 1),
type = "l", col = "black", ylab = "transformation",
las = 1, main = "extlogitlink(p, min = 0.2, max = 0.6)")
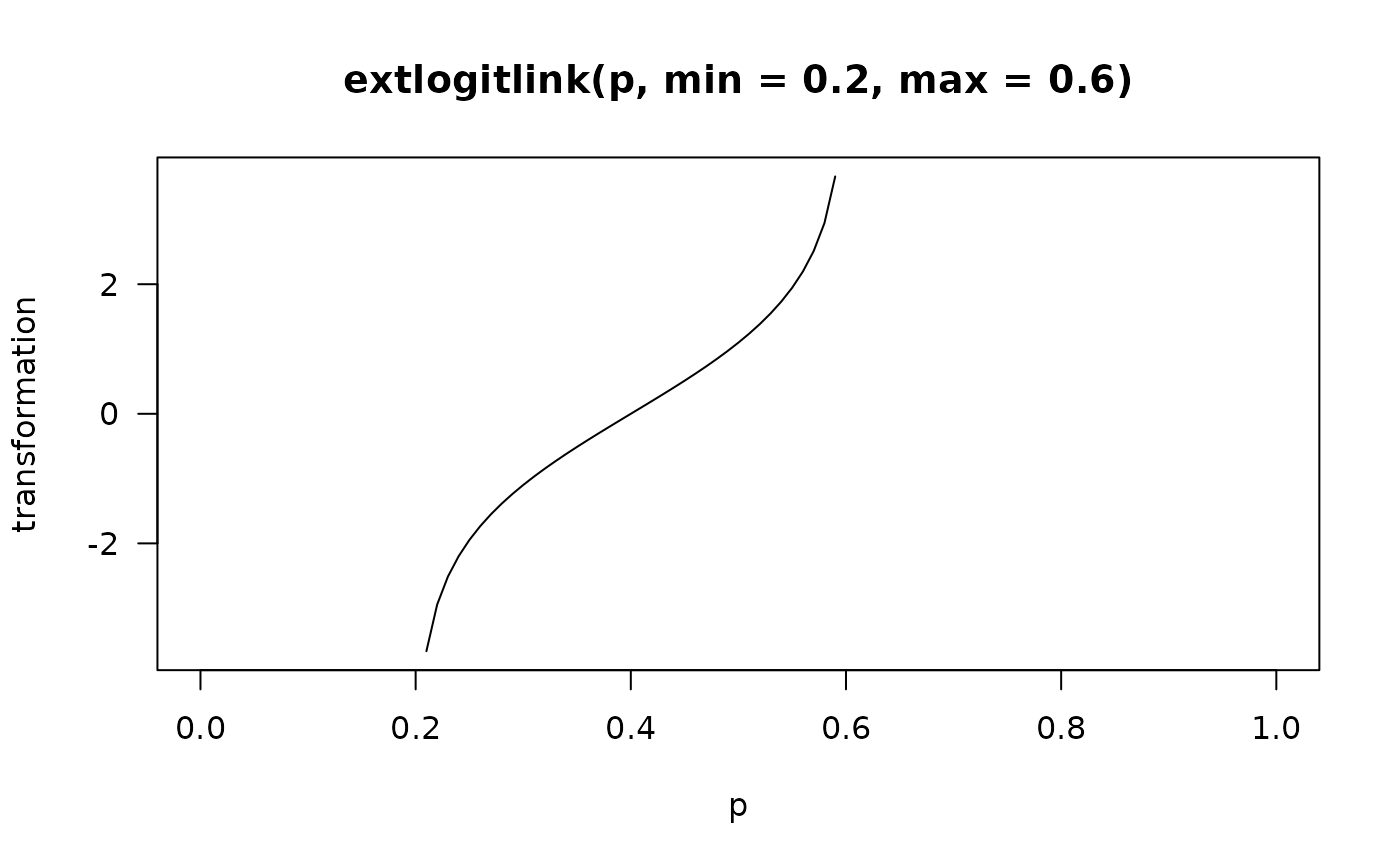 par(lwd = 1)
# \dontrun{}
par(lwd = 1)
# \dontrun{}