The Lomax Distribution
lomaxUC.RdDensity, distribution function, quantile function and random
generation for the Lomax distribution with scale parameter
scale and shape parameter q.
dlomax(x, scale = 1, shape3.q, log = FALSE)
plomax(q, scale = 1, shape3.q, lower.tail = TRUE, log.p = FALSE)
qlomax(p, scale = 1, shape3.q, lower.tail = TRUE, log.p = FALSE)
rlomax(n, scale = 1, shape3.q)Arguments
Value
dlomax gives the density,
plomax gives the distribution function,
qlomax gives the quantile function, and
rlomax generates random deviates.
References
Kleiber, C. and Kotz, S. (2003). Statistical Size Distributions in Economics and Actuarial Sciences, Hoboken, NJ, USA: Wiley-Interscience.
Details
See lomax, which is the VGAM family function
for estimating the parameters by maximum likelihood estimation.
Note
The Lomax distribution is a special case of the 4-parameter generalized beta II distribution.
Examples
probs <- seq(0.1, 0.9, by = 0.1)
max(abs(plomax(qlomax(p = probs, shape3.q = 1),
shape3.q = 1) - probs)) # Should be 0
#> [1] 5.551115e-17
if (FALSE) par(mfrow = c(1, 2))
x <- seq(-0.01, 5, len = 401)
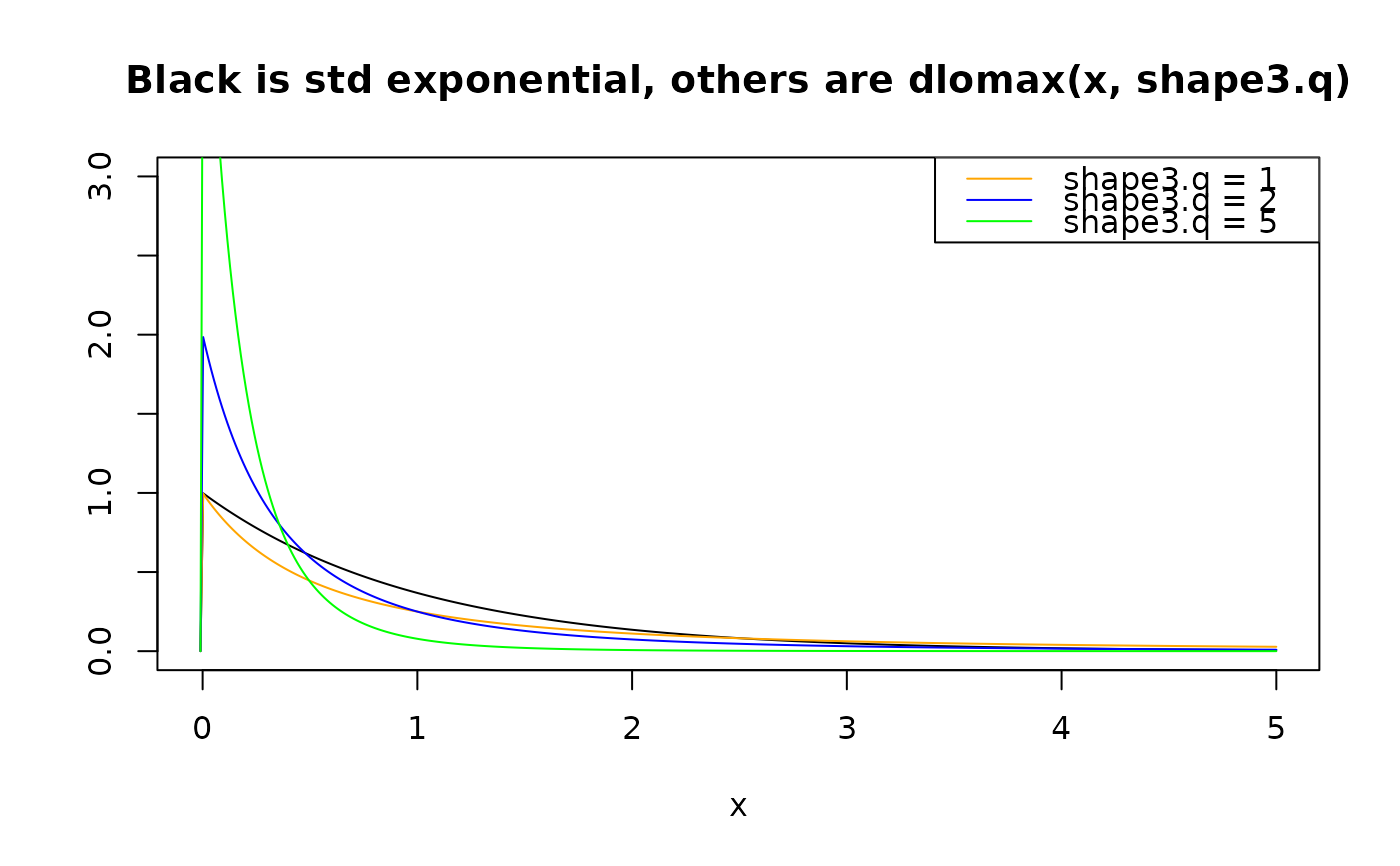
plot(x, dexp(x), type = "l", col = "black", ylab = "", ylim = c(0, 3),
main = "Black is std exponential, others are dlomax(x, shape3.q)")
lines(x, dlomax(x, shape3.q = 1), col = "orange")
lines(x, dlomax(x, shape3.q = 2), col = "blue")
lines(x, dlomax(x, shape3.q = 5), col = "green")
legend("topright", col = c("orange","blue","green"), lty = rep(1, 3),
legend = paste("shape3.q =", c(1, 2, 5)))
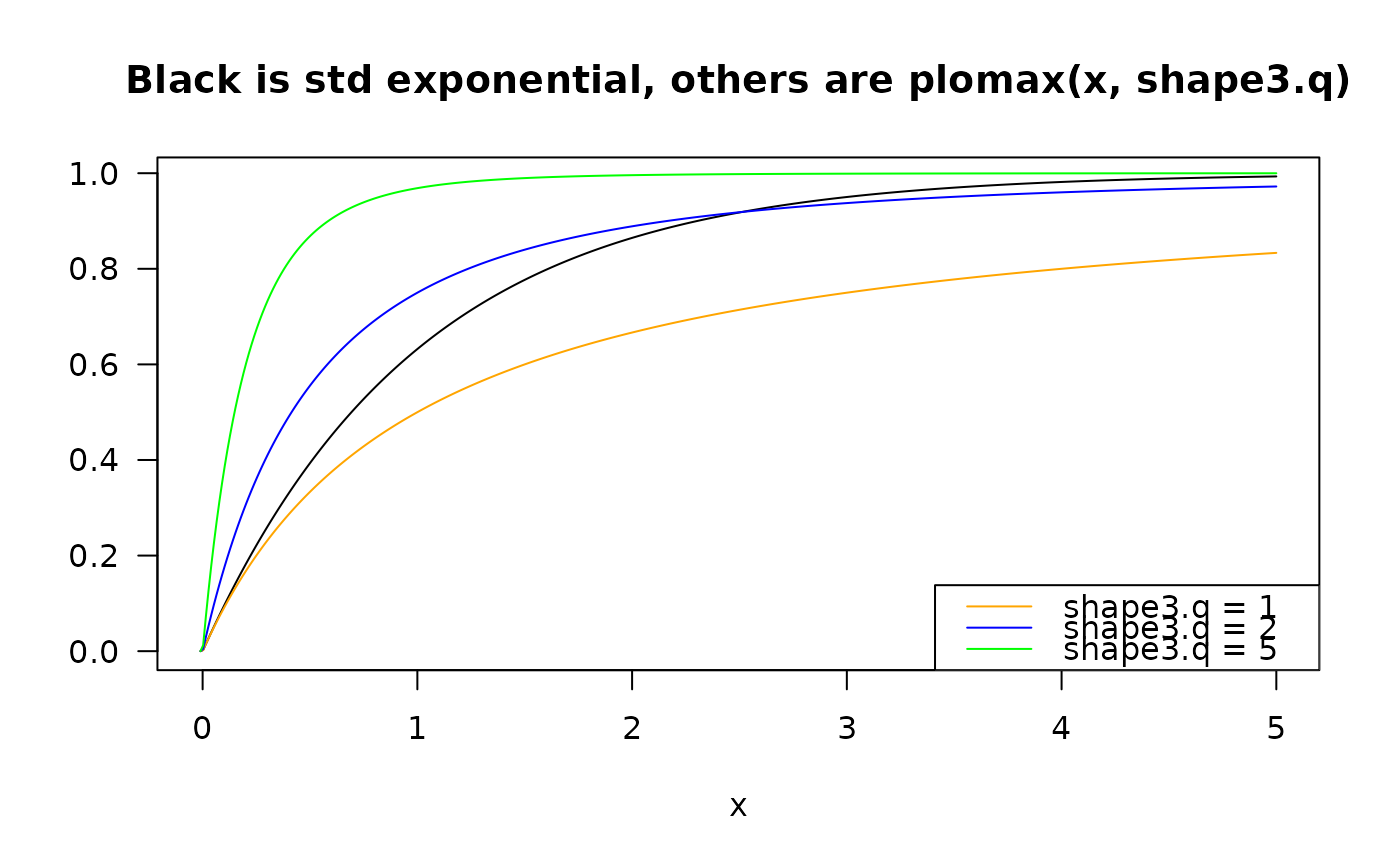
 plot(x, pexp(x), type = "l", col = "black", ylab = "", las = 1,
main = "Black is std exponential, others are plomax(x, shape3.q)")
lines(x, plomax(x, shape3.q = 1), col = "orange")
lines(x, plomax(x, shape3.q = 2), col = "blue")
lines(x, plomax(x, shape3.q = 5), col = "green")
legend("bottomright", col = c("orange","blue","green"), lty = rep(1, 3),
legend = paste("shape3.q =", c(1, 2, 5)))
plot(x, pexp(x), type = "l", col = "black", ylab = "", las = 1,
main = "Black is std exponential, others are plomax(x, shape3.q)")
lines(x, plomax(x, shape3.q = 1), col = "orange")
lines(x, plomax(x, shape3.q = 2), col = "blue")
lines(x, plomax(x, shape3.q = 5), col = "green")
legend("bottomright", col = c("orange","blue","green"), lty = rep(1, 3),
legend = paste("shape3.q =", c(1, 2, 5)))
 # \dontrun{}
# \dontrun{}