Ever used an R function that produced a not-very-helpful error message, just to discover after minutes of debugging that you simply passed a wrong argument?
Blaming the laziness of the package author for not doing such standard checks (in a dynamically typed language such as R) is at least partially unfair, as R makes these types of checks cumbersome and annoying. Well, that’s how it was in the past.
Enter checkmate.
Virtually every standard type of user error when passing arguments into function can be caught with a simple, readable line which produces an informative error message in case. A substantial part of the package was written in C to minimize any worries about execution time overhead.
Intro
As a motivational example, consider you have a function to calculate the faculty of a natural number and the user may choose between using either the stirling approximation or R’s factorial function (which internally uses the gamma function). Thus, you have two arguments, n and method. Argument n must obviously be a positive natural number and method must be either "stirling" or "factorial". Here is a version of all the hoops you need to jump through to ensure that these simple requirements are met:
fact <- function(n, method = "stirling") {
if (length(n) != 1)
stop("Argument 'n' must have length 1")
if (!is.numeric(n))
stop("Argument 'n' must be numeric")
if (is.na(n))
stop("Argument 'n' may not be NA")
if (is.double(n)) {
if (is.nan(n))
stop("Argument 'n' may not be NaN")
if (is.infinite(n))
stop("Argument 'n' must be finite")
if (abs(n - round(n, 0)) > sqrt(.Machine$double.eps))
stop("Argument 'n' must be an integerish value")
n <- as.integer(n)
}
if (n < 0)
stop("Argument 'n' must be >= 0")
if (length(method) != 1)
stop("Argument 'method' must have length 1")
if (!is.character(method) || !method %in% c("stirling", "factorial"))
stop("Argument 'method' must be either 'stirling' or 'factorial'")
if (method == "factorial")
factorial(n)
else
sqrt(2 * pi * n) * (n / exp(1))^n
}And for comparison, here is the same function using checkmate:
fact <- function(n, method = "stirling") {
assertCount(n)
assertChoice(method, c("stirling", "factorial"))
if (method == "factorial")
factorial(n)
else
sqrt(2 * pi * n) * (n / exp(1))^n
}Function overview
The functions can be split into four functional groups, indicated by their prefix.
If prefixed with assert, an error is thrown if the corresponding check fails. Otherwise, the checked object is returned invisibly. There are many different coding styles out there in the wild, but most R programmers stick to either camelBack or underscore_case. Therefore, checkmate offers all functions in both flavors: assert_count is just an alias for assertCount but allows you to retain your favorite style.
The family of functions prefixed with test always return the check result as logical value. Again, you can use test_count and testCount interchangeably.
Functions starting with check return the error message as a string (or TRUE otherwise) and can be used if you need more control and, e.g., want to grep on the returned error message.
expect is the last family of functions and is intended to be used with the testthat package. All performed checks are logged into the testthat reporter. Because testthat uses the underscore_case, the extension functions only come in the underscore style.
All functions are categorized into objects to check on the package help page.
In case you miss flexibility
You can use assert to perform multiple checks at once and throw an assertion if all checks fail.
Here is an example where we check that x is either of class foo or class bar:
f <- function(x) {
assert(
checkClass(x, "foo"),
checkClass(x, "bar")
)
}Note that assert(, combine = "or") and assert(, combine = "and") allow to control the logical combination of the specified checks, and that the former is the default.
Argument Checks for the Lazy
The following functions allow a special syntax to define argument checks using a special format specification. E.g., qassert(x, "I+") asserts that x is an integer vector with at least one element and no missing values. This very simple domain specific language covers a large variety of frequent argument checks with only a few keystrokes. You choose what you like best.
checkmate as testthat extension
To extend testthat, you need to IMPORT, DEPEND or SUGGEST on the checkmate package. Here is a minimal example:
# file: tests/test-all.R
library(testthat)
library(checkmate) # for testthat extensions
test_check("mypkg")Now you are all set and can use more than 30 new expectations in your tests.
test_that("checkmate is a sweet extension for testthat", {
x = runif(100)
expect_numeric(x, len = 100, any.missing = FALSE, lower = 0, upper = 1)
# or, equivalent, using the lazy style:
qexpect(x, "N100[0,1]")
})Speed considerations
In comparison with tediously writing the checks yourself in R (c.f. factorial example at the beginning of the vignette), R is sometimes a tad faster while performing checks on scalars. This seems odd at first, because checkmate is mostly written in C and should be comparably fast. Yet many of the functions in the base package are not regular functions, but primitives. While primitives jump directly into the C code, checkmate has to use the considerably slower .Call interface. As a result, it is possible to write (very simple) checks using only the base functions which, under some circumstances, slightly outperform checkmate. However, if you go one step further and wrap the custom check into a function to convenient re-use it, the performance gain is often lost (see benchmark 1).
For larger objects the tide has turned because checkmate avoids many unnecessary intermediate variables. Also note that the quick/lazy implementation in qassert/qtest/qexpect is often a tad faster because only two arguments have to be evaluated (the object and the rule) to determine the set of checks to perform.
Below you find some (probably unrepresentative) benchmark. But also note that this one here has been executed from inside knitr which is often the cause for outliers in the measured execution time. Better run the benchmark yourself to get unbiased results.
Benchmark 1: Assert that x is a flag
library(checkmate)
library(ggplot2)
library(microbenchmark)
x = TRUE
r = function(x, na.ok = FALSE) { stopifnot(is.logical(x), length(x) == 1, na.ok || !is.na(x)) }
cm = function(x) assertFlag(x)
cmq = function(x) qassert(x, "B1")
mb = microbenchmark(r(x), cm(x), cmq(x))
print(mb)## Unit: microseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval
## r(x) 4.450 5.0095 37.51047 5.2355 5.4615 3209.290 100
## cm(x) 2.732 3.4620 18.98496 3.6610 3.8900 1326.472 100
## cmq(x) 1.700 2.2700 13.59707 2.4065 2.5285 1040.475 100
autoplot(mb)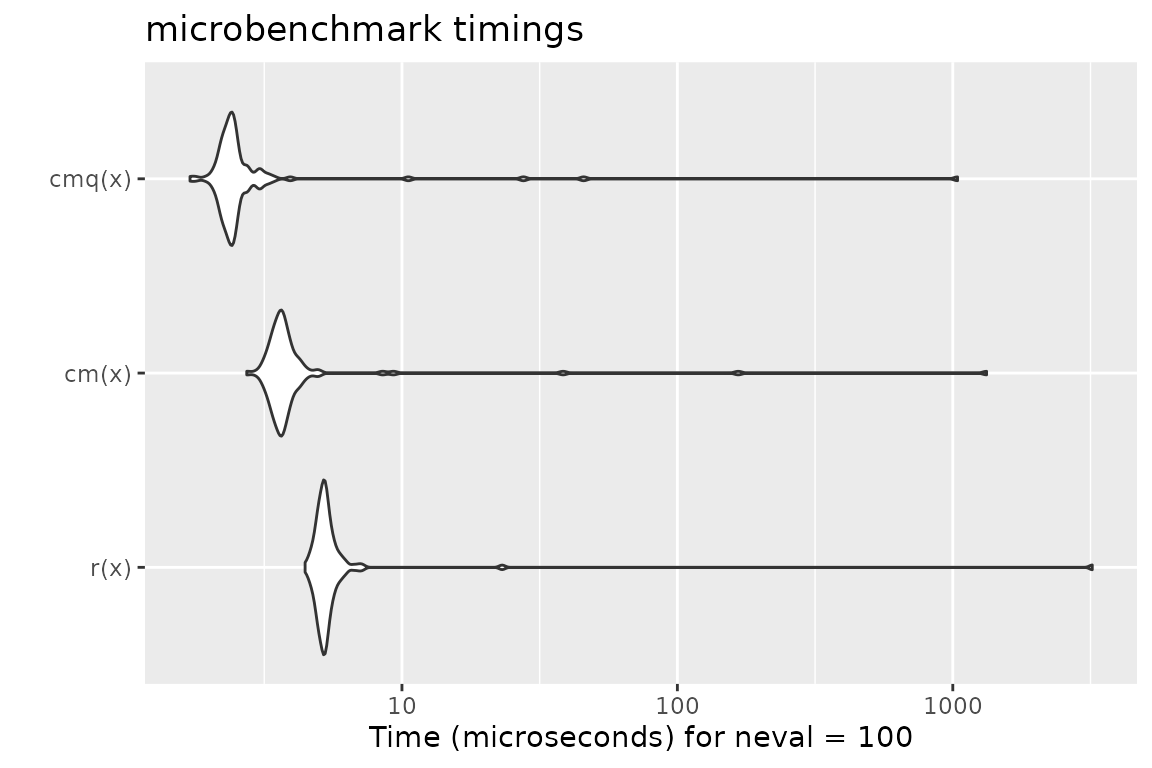
Benchmark 2: Assert that x is a numeric of length 1000 with no missing nor NaN values
x = runif(1000)
r = function(x) stopifnot(is.numeric(x), length(x) == 1000, all(!is.na(x) & x >= 0 & x <= 1))
cm = function(x) assertNumeric(x, len = 1000, any.missing = FALSE, lower = 0, upper = 1)
cmq = function(x) qassert(x, "N1000[0,1]")
mb = microbenchmark(r(x), cm(x), cmq(x))
print(mb)## Unit: microseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval
## r(x) 11.662 18.7040 71.41568 19.6035 20.4425 5154.376 100
## cm(x) 5.722 8.2985 21.52800 8.6870 9.1875 1181.172 100
## cmq(x) 4.377 6.5665 19.08633 6.8970 7.2255 1216.398 100
autoplot(mb)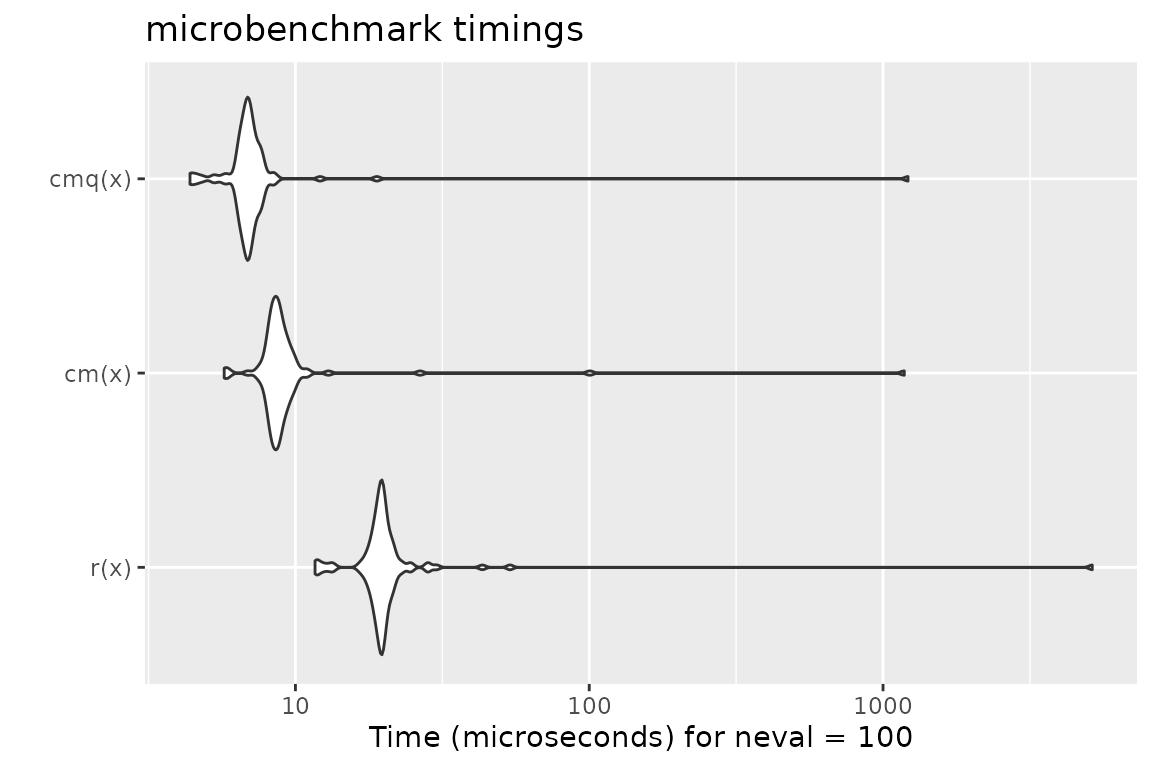
Benchmark 3: Assert that x is a character vector with no missing values nor empty strings
x = sample(letters, 10000, replace = TRUE)
r = function(x) stopifnot(is.character(x), !any(is.na(x)), all(nchar(x) > 0))
cm = function(x) assertCharacter(x, any.missing = FALSE, min.chars = 1)
cmq = function(x) qassert(x, "S+[1,]")
mb = microbenchmark(r(x), cm(x), cmq(x))
print(mb)## Unit: microseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval
## r(x) 227.559 255.9450 384.3425 299.7525 496.4410 2183.536 100
## cm(x) 89.682 103.2540 133.6970 130.9875 147.5585 789.532 100
## cmq(x) 119.577 129.0835 154.4696 145.1485 162.1350 1031.045 100
autoplot(mb)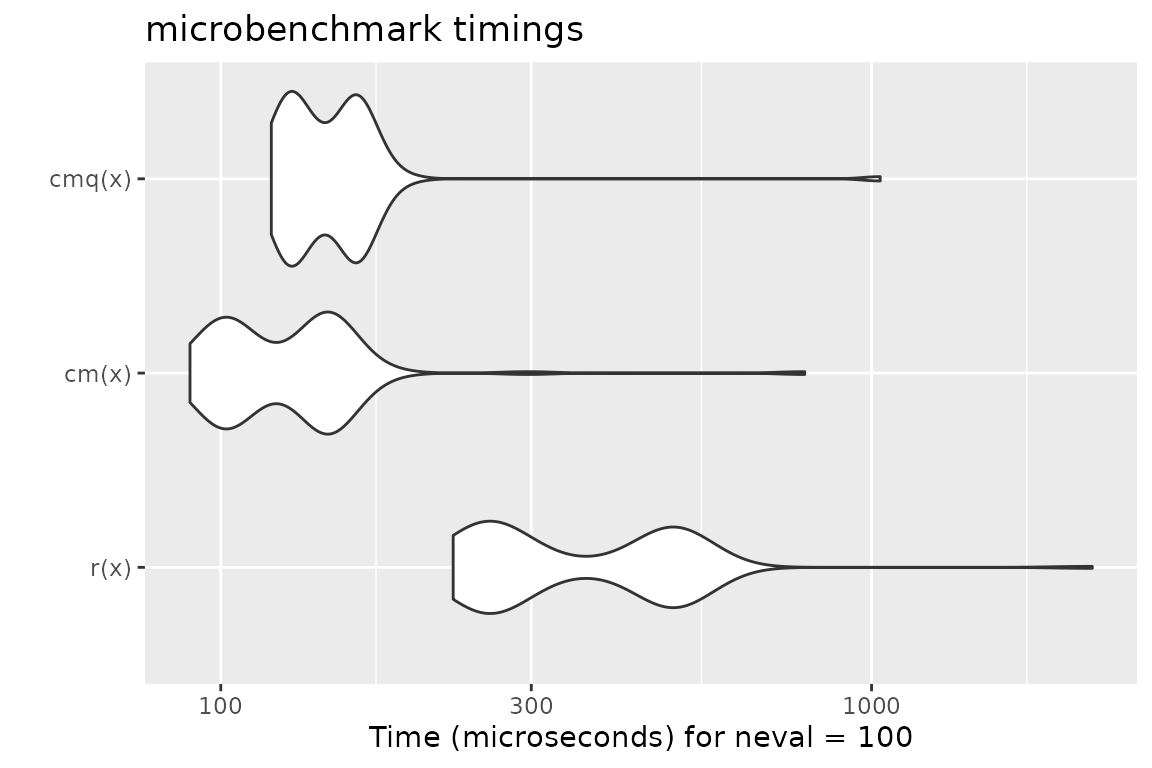
Benchmark 4: Test that x is a data frame with no missing values
N = 10000
x = data.frame(a = runif(N), b = sample(letters[1:5], N, replace = TRUE), c = sample(c(FALSE, TRUE), N, replace = TRUE))
r = function(x) is.data.frame(x) && !any(sapply(x, function(x) any(is.na(x))))
cm = function(x) testDataFrame(x, any.missing = FALSE)
cmq = function(x) qtest(x, "D")
mb = microbenchmark(r(x), cm(x), cmq(x))
print(mb)## Unit: microseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval
## r(x) 56.227 59.4235 94.04374 60.7030 65.8890 2679.350 100
## cm(x) 30.262 32.5525 47.11006 33.3375 35.1630 982.930 100
## cmq(x) 25.256 26.8655 36.50067 26.9680 27.3095 669.967 100
autoplot(mb)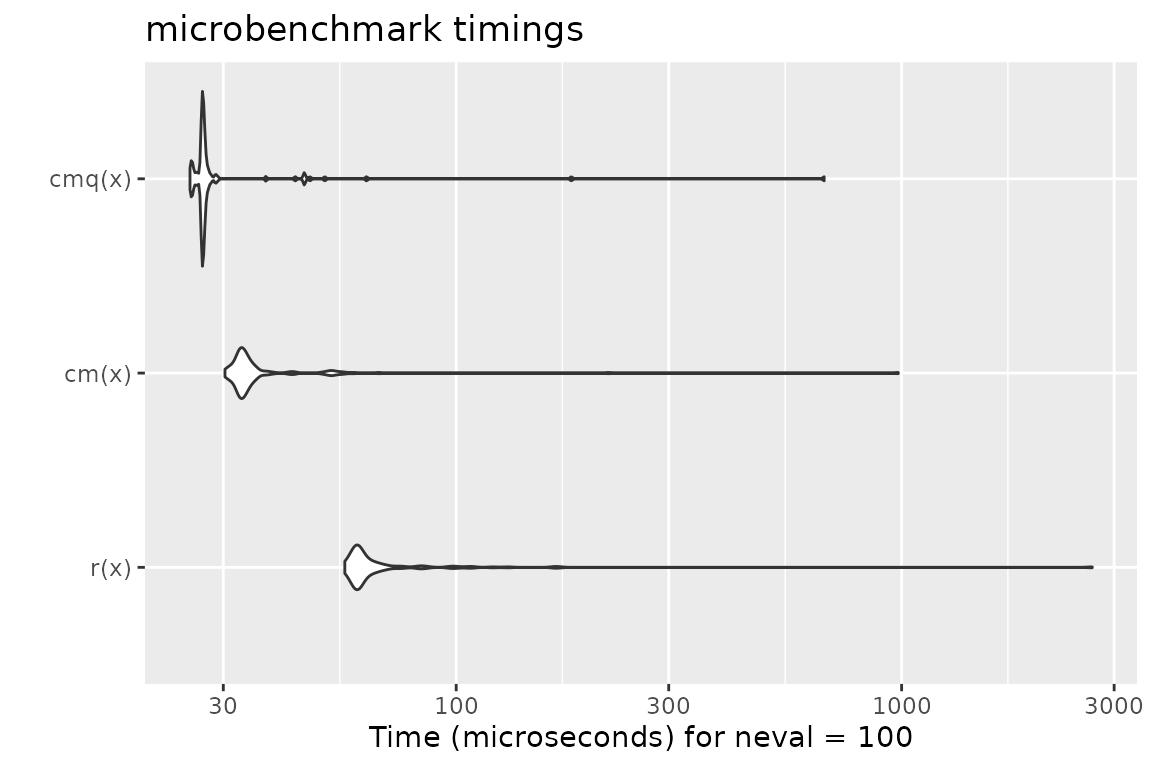
# checkmate tries to stop as early as possible
x$a[1] = NA
mb = microbenchmark(r(x), cm(x), cmq(x))
print(mb)## Unit: microseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval
## r(x) 71.731 87.2500 219.23656 90.1265 92.7450 10342.041 100
## cm(x) 7.018 7.8955 10.00059 8.3530 9.8835 54.143 100
## cmq(x) 1.229 1.6595 2.15437 1.7650 2.0240 9.434 100
autoplot(mb)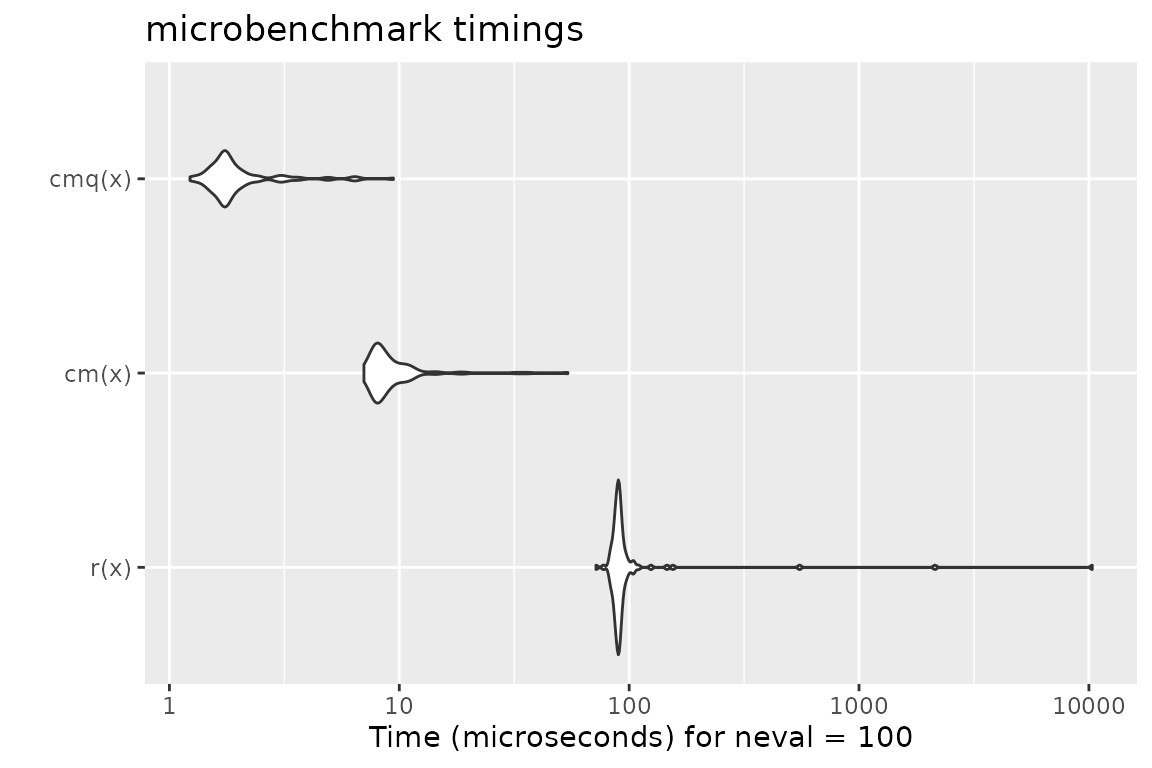
Benchmark 5: Assert that x is an increasing sequence of integers with no missing values
N = 10000
x.altrep = seq_len(N) # this is an ALTREP in R version >= 3.5.0
x.sexp = c(x.altrep) # this is a regular SEXP OTOH
r = function(x) stopifnot(is.integer(x), !any(is.na(x)), !is.unsorted(x))
cm = function(x) assertInteger(x, any.missing = FALSE, sorted = TRUE)
mb = microbenchmark(r(x.sexp), cm(x.sexp), r(x.altrep), cm(x.altrep))
print(mb)## Unit: microseconds
## expr min lq mean median uq max neval
## r(x.sexp) 24.156 28.5525 51.69289 28.9595 31.4550 2111.743 100
## cm(x.sexp) 10.189 10.9135 22.35065 11.1630 11.7595 1035.598 100
## r(x.altrep) 29.505 31.5215 34.48006 31.9465 34.3105 64.761 100
## cm(x.altrep) 2.844 3.1465 5.13973 3.3750 4.4795 123.260 100
autoplot(mb)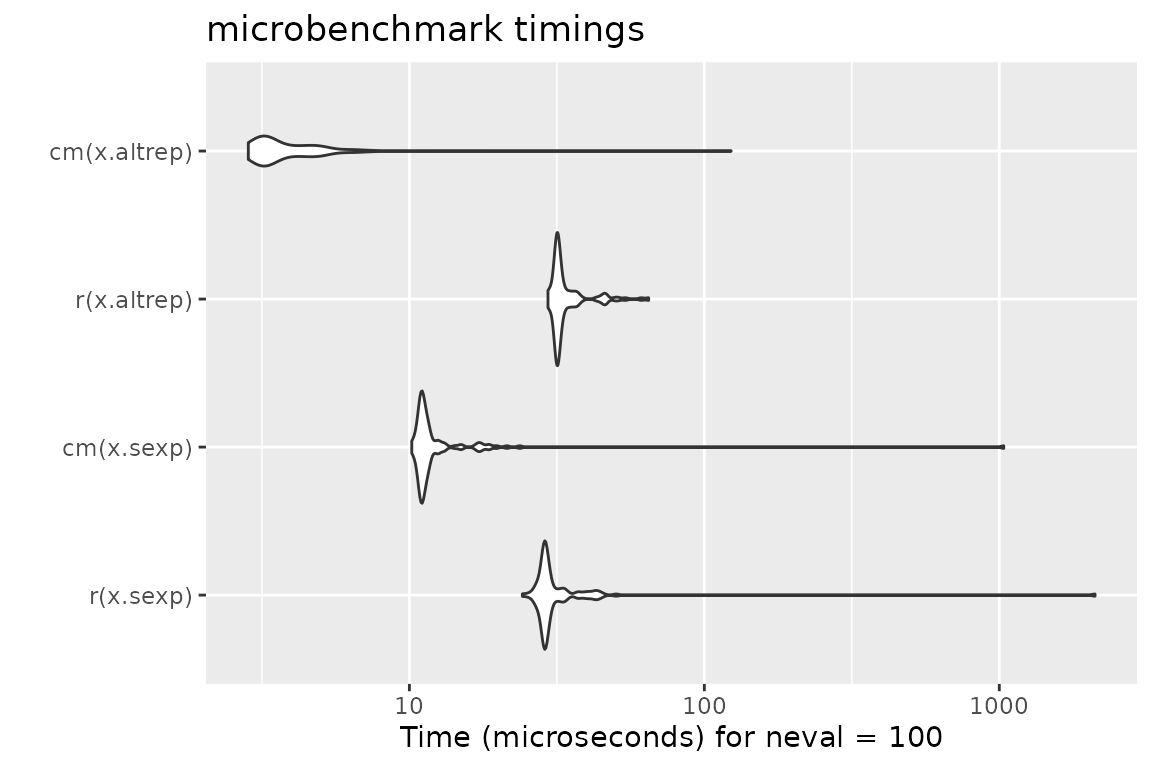
Extending checkmate
To extend checkmate a custom check* function has to be written. For example, to check for a square matrix one can re-use parts of checkmate and extend the check with additional functionality:
checkSquareMatrix = function(x, mode = NULL) {
# check functions must return TRUE on success
# and a custom error message otherwise
res = checkMatrix(x, mode = mode)
if (!isTRUE(res))
return(res)
if (nrow(x) != ncol(x))
return("Must be square")
return(TRUE)
}
# a quick test:
X = matrix(1:9, nrow = 3)
checkSquareMatrix(X)## [1] TRUE
checkSquareMatrix(X, mode = "character")## [1] "Must store characters"
checkSquareMatrix(X[1:2, ])## [1] "Must be square"The respective counterparts to the check-function can be created using the constructors makeAssertionFunction, makeTestFunction and makeExpectationFunction:
# For assertions:
assert_square_matrix = assertSquareMatrix = makeAssertionFunction(checkSquareMatrix)
print(assertSquareMatrix)## function (x, mode = NULL, .var.name = checkmate::vname(x), add = NULL)
## {
## if (missing(x))
## stop(sprintf("argument \"%s\" is missing, with no default",
## .var.name))
## res = checkSquareMatrix(x, mode)
## checkmate::makeAssertion(x, res, .var.name, add)
## }
# For tests:
test_square_matrix = testSquareMatrix = makeTestFunction(checkSquareMatrix)
print(testSquareMatrix)## function (x, mode = NULL)
## {
## isTRUE(checkSquareMatrix(x, mode))
## }
# For expectations:
expect_square_matrix = makeExpectationFunction(checkSquareMatrix)
print(expect_square_matrix)## function (x, mode = NULL, info = NULL, label = vname(x))
## {
## if (missing(x))
## stop(sprintf("Argument '%s' is missing", label))
## res = checkSquareMatrix(x, mode)
## makeExpectation(x, res, info, label)
## }Note that all the additional arguments .var.name, add, info and label are automatically joined with the function arguments of your custom check function. Also note that if you define these functions inside an R package, the constructors are called at build-time (thus, there is no negative impact on the runtime).
Calling checkmate from C/C++
The package registers two functions which can be used in other packages’ C/C++ code for argument checks.
SEXP qassert(SEXP x, const char *rule, const char *name);
Rboolean qtest(SEXP x, const char *rule);These are the counterparts to qassert and qtest. Due to their simplistic interface, they perfectly suit the requirements of most type checks in C/C++.
For detailed background information on the register mechanism, see the Exporting C Code section in Hadley’s Book “R Packages” or WRE. Here is a step-by-step guide to get you started:
- Add
checkmateto your “Imports” and “LinkingTo” sections in your DESCRIPTION file. - Create a stub C source file
"checkmate_stub.c", see below. - Include the provided header file
<checkmate.h>in each compilation unit where you want to use checkmate.
File contents for (2):
#include <checkmate.h>
#include <checkmate_stub.c>Session Info
For the sake of completeness, here the sessionInfo() for the benchmark (but remember the note before on knitr possibly biasing the results).
## R version 4.4.1 (2024-06-14)
## Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
## Running under: Ubuntu 22.04.5 LTS
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
## LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.20.so; LAPACK version 3.10.0
##
## locale:
## [1] LC_CTYPE=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C
## [3] LC_TIME=en_US.UTF-8 LC_COLLATE=en_US.UTF-8
## [5] LC_MONETARY=en_US.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=en_US.UTF-8
## [7] LC_PAPER=en_US.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C
## [9] LC_ADDRESS=C LC_TELEPHONE=C
## [11] LC_MEASUREMENT=en_US.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
##
## time zone: Etc/UTC
## tzcode source: system (glibc)
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] microbenchmark_1.5.0 ggplot2_3.5.2 checkmate_2.3.3
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] vctrs_0.6.5 cli_3.6.5 knitr_1.50 rlang_1.1.6
## [5] xfun_0.53 textshaping_1.0.1 jsonlite_2.0.0 glue_1.8.0
## [9] backports_1.5.0 htmltools_0.5.8.1 ragg_1.4.0 sass_0.4.10
## [13] scales_1.4.0 rmarkdown_2.29 grid_4.4.1 tibble_3.3.0
## [17] evaluate_1.0.4 jquerylib_0.1.4 fastmap_1.2.0 yaml_2.3.10
## [21] lifecycle_1.0.4 compiler_4.4.1 RColorBrewer_1.1-3 fs_1.6.6
## [25] pkgconfig_2.0.3 htmlwidgets_1.6.4 farver_2.1.2 systemfonts_1.2.3
## [29] digest_0.6.37 R6_2.6.1 pillar_1.11.0 magrittr_2.0.3
## [33] bslib_0.9.0 withr_3.0.2 gtable_0.3.6 tools_4.4.1
## [37] pkgdown_2.1.3 cachem_1.1.0 desc_1.4.3