Run FlexMix Repeatedly
stepFlexmix.RdRuns flexmix repeatedly for different numbers of components and returns the maximum likelihood solution for each.
initFlexmix(..., k, init = list(), control = list(), nrep = 3L,
verbose = TRUE, drop = TRUE, unique = FALSE)
initMethod(name = c("tol.em", "cem.em", "sem.em"),
step1 = list(tolerance = 10^-2),
step2 = list(), control = list(), nrep = 3L)
stepFlexmix(..., k = NULL, nrep = 3, verbose = TRUE, drop = TRUE,
unique = FALSE)
# S4 method for class 'stepFlexmix,missing'
plot(x, y, what = c("AIC", "BIC", "ICL"),
xlab = NULL, ylab = NULL, legend = "topright", ...)
# S4 method for class 'stepFlexmix'
getModel(object, which = "BIC")
# S4 method for class 'stepFlexmix'
unique(x, incomparables = FALSE, ...)Arguments
- ...
- k
A vector of integers passed in turn to the
kargument offlexmix.- init
An object of class
"initMethod"or a named list whereinitMethodis called with it as arguments in addition to thecontrolargument.- name
A character string indication which initialization strategy should be employed: short runs of EM followed by a long (
"tol.em"), short runs of CEM followed by a long EM run ("cem.em"), short runs of SEM followed by a long EM run ("sem.em").- step1
A named list which combined with the
controlargument is coercable to a"FLXcontrol"object. This control setting is used for the short runs.- step2
A named list which combined with the
controlargument is coercable to a"FLXcontrol"object. This control setting is used for the long run.- control
A named list which combined with the
step1or thestep2argument is coercable to a"FLXcontrol"object.- nrep
For each value of
krunflexmixnreptimes and keep only the solution with maximum likelihood. Ifnrepis set for the long run, it is ignored, because the EM algorithm is deterministic using the best solution discovered in the short runs for initialization.- verbose
If
TRUE, show progress information during computations.- drop
If
TRUEandkis of length 1, then a single flexmix object is returned instead of a"stepFlexmix"object.- unique
If
TRUE, thenunique()is called on the result, see below.- x, object
An object of class
"stepFlexmix".- y
Not used.
- what
Character vector naming information criteria to plot. Functions of the same name must exist, which take a
stepFlexmixobject as input and return a numeric vector likeAIC,stepFlexmix-method(see examples below).- xlab,ylab
Graphical parameters.
- legend
If not
FALSEandwhatcontains more than 1 element, a legend is placed at the specified location, seelegendfor details.- which
Number of model to get. If character, interpreted as number of components or name of an information criterion.
- incomparables
A vector of values that cannot be compared. Currently,
FALSEis the only possible value, meaning that all values can be compared.
Value
An object of class "stepFlexmix" containing the best models
with respect to the log likelihood for the different number of
components in a slot if length(k)>1, else directly an object of
class "flexmix".
If unique = FALSE, then the resulting object contains one
model per element of k (which is the number of clusters the EM
algorithm started with). If unique = TRUE, then the result
is resorted according to the number of clusters contained in the
fitted models (which may be less than the number with which the EM
algorithm started), and only the maximum likelihood solution for each
number of fitted clusters is kept. This operation can also be done
manually by calling unique() on objects of class
"stepFlexmix".
References
Friedrich Leisch. FlexMix: A general framework for finite mixture models and latent class regression in R. Journal of Statistical Software, 11(8), 2004. doi:10.18637/jss.v011.i08
Christophe Biernacki, Gilles Celeux and Gerard Govaert. Choosing starting values for the EM algorithm for getting the highest likelihood in multivariate Gaussian mixture models. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 41(3–4), 561–575, 2003.
Theresa Scharl, Bettina Gruen and Friedrch Leisch. Mixtures of regression models for time-course gene expression data: Evaluation of initialization and random effects. Bioinformatics, 26(3), 370–377, 2010.
Examples
data("Nclus", package = "flexmix")
## try 2 times for k = 4
set.seed(511)
ex1 <- initFlexmix(Nclus~1, k = 4, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
nrep = 2)
#> 4 : * *
ex1
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 4, nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2 3 4
#> 204 100 150 96
#>
#> convergence after 35 iterations
## now 2 times each for k = 2:5, specify control parameter
ex2 <- initFlexmix(Nclus~1, k = 2:5, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#> 2 : * *
#> 3 : * *
#> 4 : * *
#> 5 : * *
#> * * * *
ex2
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2:5, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
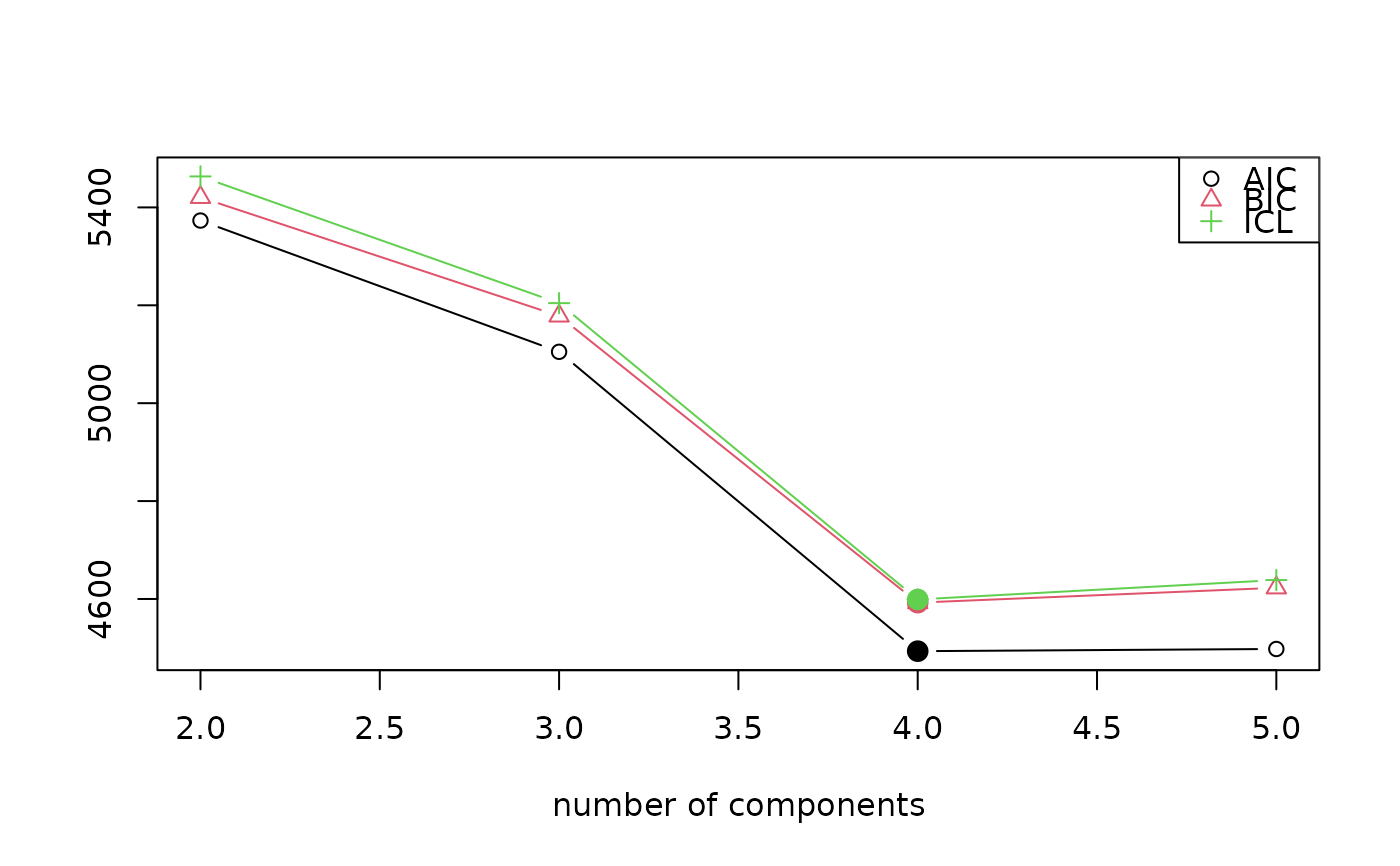
#> iter converged k k0 logLik AIC BIC ICL
#> 2 42 TRUE 2 2 -2675.576 5373.153 5420.562 5463.294
#> 3 51 TRUE 3 3 -2535.489 5104.977 5178.246 5204.401
#> 4 29 TRUE 4 4 -2223.677 4493.355 4592.483 4599.016
#> 5 75 TRUE 5 5 -2219.906 4497.812 4622.800 4638.652
plot(ex2)
 ## get BIC values
BIC(ex2)
#> 2 3 4 5
#> 5420.562 5178.246 4592.483 4622.800
## get smallest model
getModel(ex2, which = 1)
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2
#> 369 181
#>
#> convergence after 42 iterations
## get model with 3 components
getModel(ex2, which = "3")
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 3, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2 3
#> 98 92 360
#>
#> convergence after 51 iterations
## get model with smallest ICL (here same as for AIC and BIC: true k = 4)
getModel(ex2, which = "ICL")
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 4, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2 3 4
#> 96 204 100 150
#>
#> convergence after 29 iterations
## now 1 time each for k = 2:5, with larger minimum prior
ex3 <- initFlexmix(Nclus~1, k = 2:5,
model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
control = list(minprior = 0.1), nrep = 1)
#> 2 : *
#> 3 : *
#> 4 : *
#> 5 : *
#> * * * *
ex3
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2:5, control = list(minprior = 0.1), nrep = 1)
#>
#> iter converged k k0 logLik AIC BIC ICL
#> 2 45 TRUE 2 2 -2675.577 5373.153 5420.562 5463.290
#> 3 37 TRUE 3 3 -2383.135 4800.271 4873.539 4894.960
#> 4 30 TRUE 3 4 -2404.005 4842.010 4915.278 4917.383
#> 5 31 TRUE 4 5 -2223.677 4493.355 4592.483 4599.023
## keep only maximum likelihood solution for each unique number of
## fitted clusters:
unique(ex3)
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2:5, control = list(minprior = 0.1), nrep = 1, unique = TRUE)
#>
#> iter converged k k0 logLik AIC BIC ICL
#> 2 45 TRUE 2 2 -2675.577 5373.153 5420.562 5463.290
#> 3 37 TRUE 3 3 -2383.135 4800.271 4873.539 4894.960
#> 4 31 TRUE 4 5 -2223.677 4493.355 4592.483 4599.023
## get BIC values
BIC(ex2)
#> 2 3 4 5
#> 5420.562 5178.246 4592.483 4622.800
## get smallest model
getModel(ex2, which = 1)
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2
#> 369 181
#>
#> convergence after 42 iterations
## get model with 3 components
getModel(ex2, which = "3")
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 3, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2 3
#> 98 92 360
#>
#> convergence after 51 iterations
## get model with smallest ICL (here same as for AIC and BIC: true k = 4)
getModel(ex2, which = "ICL")
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 4, control = list(minprior = 0), nrep = 2)
#>
#> Cluster sizes:
#> 1 2 3 4
#> 96 204 100 150
#>
#> convergence after 29 iterations
## now 1 time each for k = 2:5, with larger minimum prior
ex3 <- initFlexmix(Nclus~1, k = 2:5,
model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
control = list(minprior = 0.1), nrep = 1)
#> 2 : *
#> 3 : *
#> 4 : *
#> 5 : *
#> * * * *
ex3
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2:5, control = list(minprior = 0.1), nrep = 1)
#>
#> iter converged k k0 logLik AIC BIC ICL
#> 2 45 TRUE 2 2 -2675.577 5373.153 5420.562 5463.290
#> 3 37 TRUE 3 3 -2383.135 4800.271 4873.539 4894.960
#> 4 30 TRUE 3 4 -2404.005 4842.010 4915.278 4917.383
#> 5 31 TRUE 4 5 -2223.677 4493.355 4592.483 4599.023
## keep only maximum likelihood solution for each unique number of
## fitted clusters:
unique(ex3)
#>
#> Call:
#> initFlexmix(Nclus ~ 1, model = FLXMCmvnorm(diagonal = FALSE),
#> k = 2:5, control = list(minprior = 0.1), nrep = 1, unique = TRUE)
#>
#> iter converged k k0 logLik AIC BIC ICL
#> 2 45 TRUE 2 2 -2675.577 5373.153 5420.562 5463.290
#> 3 37 TRUE 3 3 -2383.135 4800.271 4873.539 4894.960
#> 4 31 TRUE 4 5 -2223.677 4493.355 4592.483 4599.023