Generate inverse Gaussian random deviates
rig.RdGenerates inverse Gaussian random deviates.
rig(n,mean,scale)Arguments
Value
A vector of inverse Gaussian random deviates.
Details
If x if the returned vector, then E(x) = mean while var(x) = scale*mean^3. For density and distribution functions
see the statmod package. The algorithm used is Algorithm 5.7 of Gentle (2003), based on Michael et al. (1976). Note that scale
here is the scale parameter in the GLM sense, which is the reciprocal of the usual `lambda' parameter.
References
Gentle, J.E. (2003) Random Number Generation and Monte Carlo Methods (2nd ed.) Springer.
Michael, J.R., W.R. Schucany & R.W. Hass (1976) Generating random variates using transformations with multiple roots. The American Statistician 30, 88-90.
Examples
require(mgcv)
set.seed(7)
## An inverse.gaussian GAM example, by modify `gamSim' output...
dat <- gamSim(1,n=400,dist="normal",scale=1)
#> Gu & Wahba 4 term additive model
dat$f <- dat$f/4 ## true linear predictor
Ey <- exp(dat$f);scale <- .5 ## mean and GLM scale parameter
## simulate inverse Gaussian response...
dat$y <- rig(Ey,mean=Ey,scale=.2)
big <- gam(y~ s(x0)+ s(x1)+s(x2)+s(x3),family=inverse.gaussian(link=log),
data=dat,method="REML")
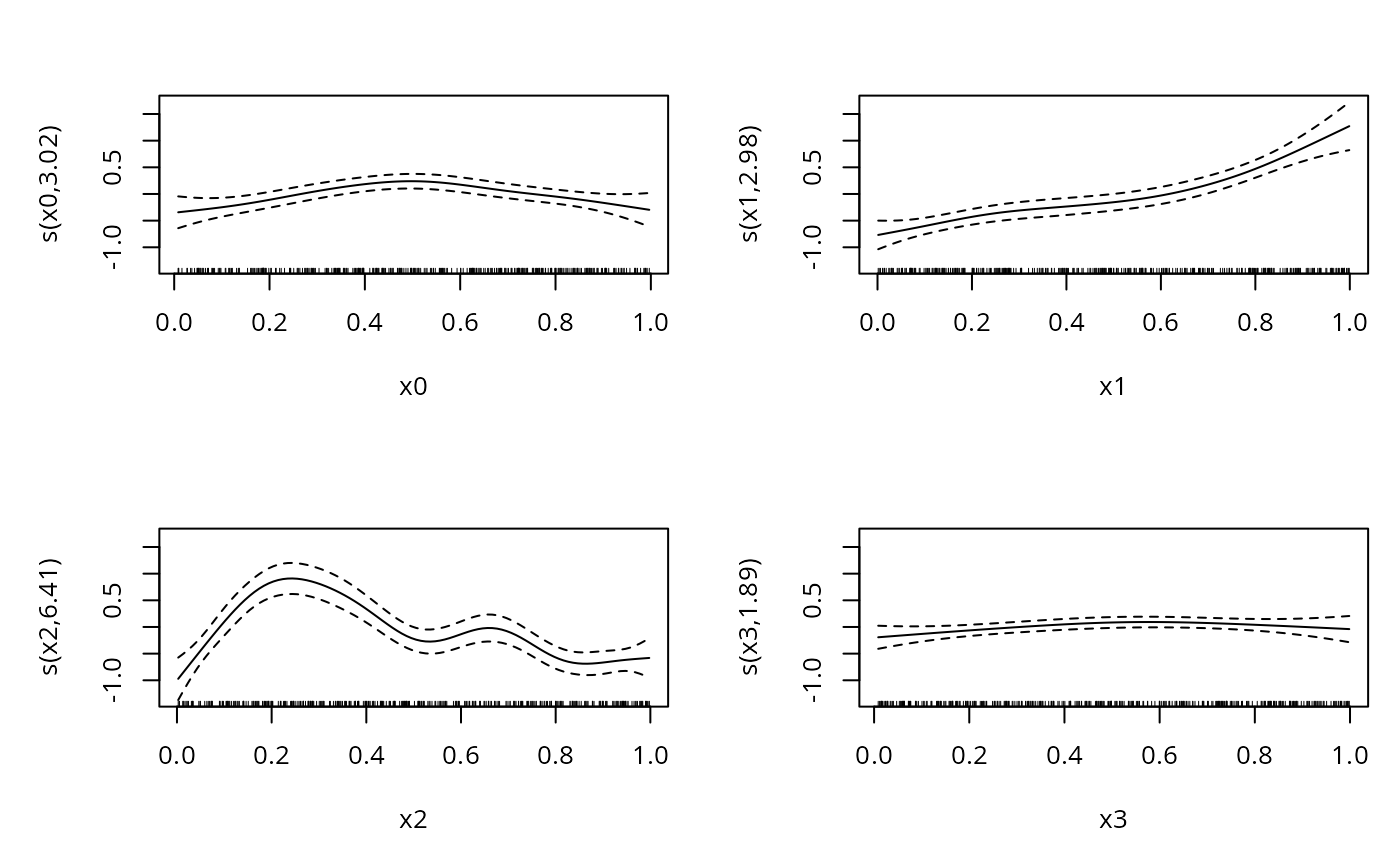
plot(big,pages=1)
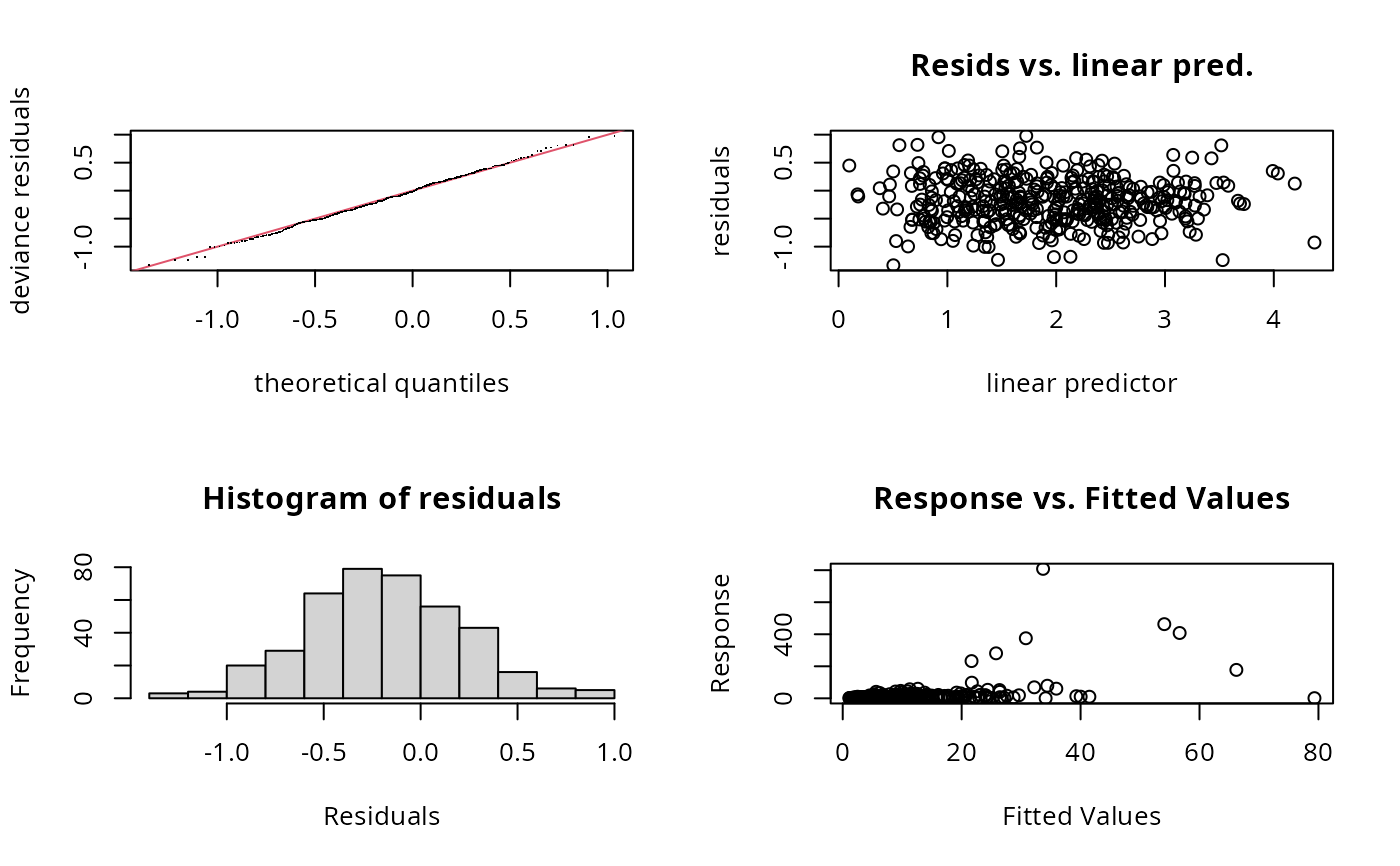
 gam.check(big)
gam.check(big)
 #>
#> Method: REML Optimizer: outer newton
#> full convergence after 8 iterations.
#> Gradient range [-0.0003256568,4.561143e-06]
#> (score 1154.207 & scale 0.1808111).
#> Hessian positive definite, eigenvalue range [0.2487389,197.5501].
#> Model rank = 37 / 37
#>
#> Basis dimension (k) checking results. Low p-value (k-index<1) may
#> indicate that k is too low, especially if edf is close to k'.
#>
#> k' edf k-index p-value
#> s(x0) 9.00 3.02 0.76 0.075 .
#> s(x1) 9.00 2.98 0.89 0.935
#> s(x2) 9.00 6.41 0.85 0.665
#> s(x3) 9.00 1.89 0.89 0.950
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
summary(big)
#>
#> Family: inverse.gaussian
#> Link function: log
#>
#> Formula:
#> y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3)
#>
#> Parametric coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 1.93014 0.06261 30.83 <2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> Approximate significance of smooth terms:
#> edf Ref.df F p-value
#> s(x0) 3.020 3.744 3.894 0.00556 **
#> s(x1) 2.985 3.712 20.371 < 2e-16 ***
#> s(x2) 6.412 7.524 12.139 < 2e-16 ***
#> s(x3) 1.887 2.343 1.637 0.16824
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> R-sq.(adj) = 0.0874 Deviance explained = 38.6%
#> -REML = 1154.2 Scale est. = 0.18081 n = 400
#>
#> Method: REML Optimizer: outer newton
#> full convergence after 8 iterations.
#> Gradient range [-0.0003256568,4.561143e-06]
#> (score 1154.207 & scale 0.1808111).
#> Hessian positive definite, eigenvalue range [0.2487389,197.5501].
#> Model rank = 37 / 37
#>
#> Basis dimension (k) checking results. Low p-value (k-index<1) may
#> indicate that k is too low, especially if edf is close to k'.
#>
#> k' edf k-index p-value
#> s(x0) 9.00 3.02 0.76 0.075 .
#> s(x1) 9.00 2.98 0.89 0.935
#> s(x2) 9.00 6.41 0.85 0.665
#> s(x3) 9.00 1.89 0.89 0.950
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
summary(big)
#>
#> Family: inverse.gaussian
#> Link function: log
#>
#> Formula:
#> y ~ s(x0) + s(x1) + s(x2) + s(x3)
#>
#> Parametric coefficients:
#> Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#> (Intercept) 1.93014 0.06261 30.83 <2e-16 ***
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> Approximate significance of smooth terms:
#> edf Ref.df F p-value
#> s(x0) 3.020 3.744 3.894 0.00556 **
#> s(x1) 2.985 3.712 20.371 < 2e-16 ***
#> s(x2) 6.412 7.524 12.139 < 2e-16 ***
#> s(x3) 1.887 2.343 1.637 0.16824
#> ---
#> Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#>
#> R-sq.(adj) = 0.0874 Deviance explained = 38.6%
#> -REML = 1154.2 Scale est. = 0.18081 n = 400